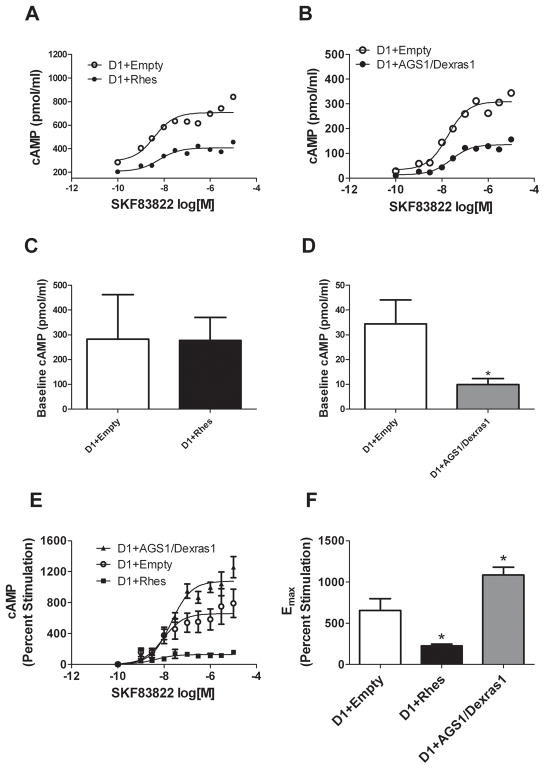
Figure 2.
Effects of Rhes and AGS1/Dexras1 on D1 receptor-induced cAMP accumulation in CHO cells. Both Rhes (A) and AGS1/Dexras1 (B) decreased SKF83822-induced cAMP accumulation when co-expressed with D1 receptors. Data are presented as mean pmol/ml cAMP (n = 5 for each of A and B). (C) Rhes did not affect basal cAMP levels (p = 0.966 by Student’s t-test, n = 5), whereas AGS1/Dexras1 (D) significantly decreased basal cAMP (*p<0.05 by Student’s t-test, n = 7). (E) Concentration-response curves for data expressed as percent stimulation of cAMP in CHO cells transfected with dopamine D1 receptors and either empty vector, AGS1/Dexras1, or Rhes. Data are mean ± SEM for percent stimulation over vehicle-treated cells. (F) Emax values (mean ± SEM) calculated from individual assays and analyzed by one-factor ANOVA and post-hoc Newman-Keuls tests. *p<0.05 versus D1+Empty. For E and F, n = 10 (D1+Empty), n = 5 (D1+ AGS1/Dexras1 and D1+Rhes).