Figure 4. Pathways of kappa light chain rearrangement and editing.
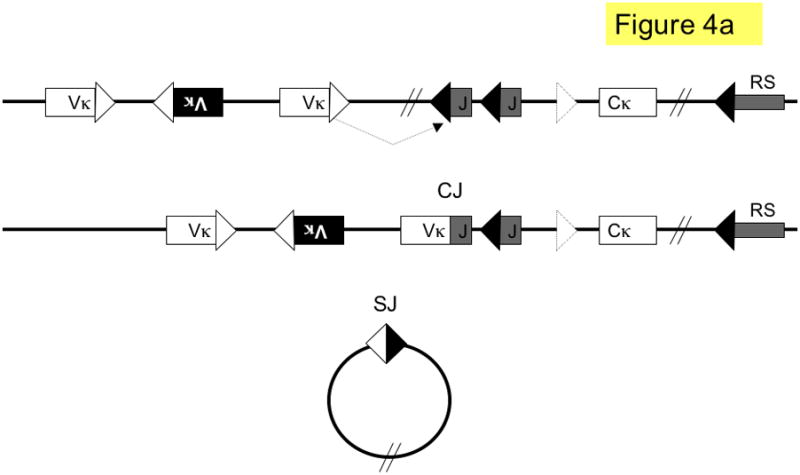
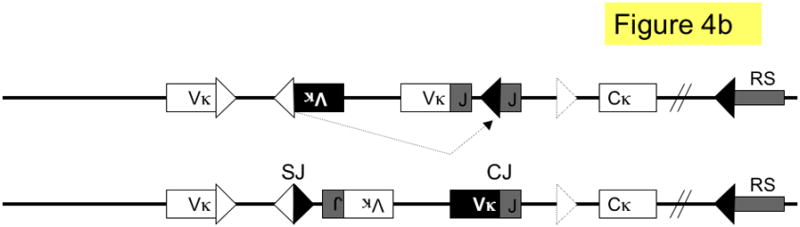
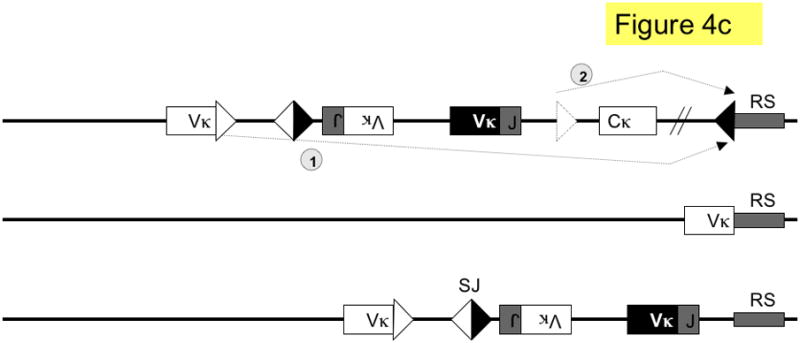
A simplified κ locus with three variable region gene segments (Vκ), two joining segments (J), one constant region (Cκ) and the recombining sequence (RS) is shown. Three different kinds of κ rearrangement are shown, which could have occurred sequentially: a. deletional κ rearrangement, producing a coding joint (CJ) and a signal joint (SJ); the piece of DNA containing the SJ is released as an episome that is not replicated with successive cell divisions. b. inversional secondary rearrangement of a Vκ gene present in reverse orientation; leapfrogging over an existing Vκ-Jκ rearrangement here produces an SJ that is retained on the chromosome in the reciprocal product; c. κ locus silencing by two pathways of RS rearrangement on a locus with at two prior Vκ-Jκ rearrangements; arrows are labeled to illustrate the two pathways: pathway 1. Vκ-RS deletional rearrangement results in excision of Cκ and pathway 2. iRS rearrangement results in excision of Cκ but retention of both preceding Vκ-Jκ rearrangements. Dashed arrows denote rearrangements, boxes represent gene segments, lines introns, white triangles recombination signal sequences with 12-nucleotide spacers, black triangles recombination signal sequences with 23-nucleotide spacers, dashed triangle J-C intron heptamer, diagonal parallel lines indicate large gaps in the intervening sequence. RS = recombining sequence.
