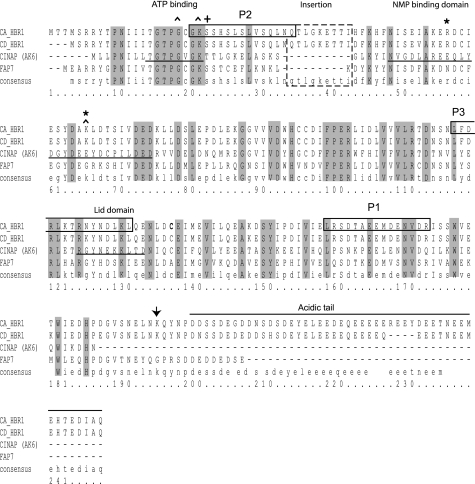
FIGURE 1.
Hbr1p amino acid sequence, predicted functional regions, and mutation sites. The 28.8-kDa amino acid sequence of Hbr1p from C. albicans is shown aligned with that of C. dubliniensis, the potential human ortholog AD-004/CINAP (coilin-interacting nuclear ATPase protein, AK-6), and the S. cerevisiae ortholog, Fap7p. The shaded areas indicate regions of identity between the four proteins. Mutations are indicated by carets and were designed to replace the consensus (K22Q) and nonconsensus (G19S) residues in the P-loop motif. A K66R mutation in the NMP-binding domain was designed to disrupt a predicted SUMO acceptor site (37). The designations for the ATP and NMP binding and the lid domains are taken from the crystal structure of CINAP (16) and are indicated by underlining. The three peptides used as epitopes for antibody production are indicated by solid boxed areas, and a Candida-specific insertion is indicated by a dashed boxed region. The lack of a terminal P-loop glycine that is a defining characteristic of the nuclear-localized group of adenylate kinase enzymes is indicated by a (+). The acidic carboxyl terminus contributes to the overall net charge of the molecule (−19.4 to −47).