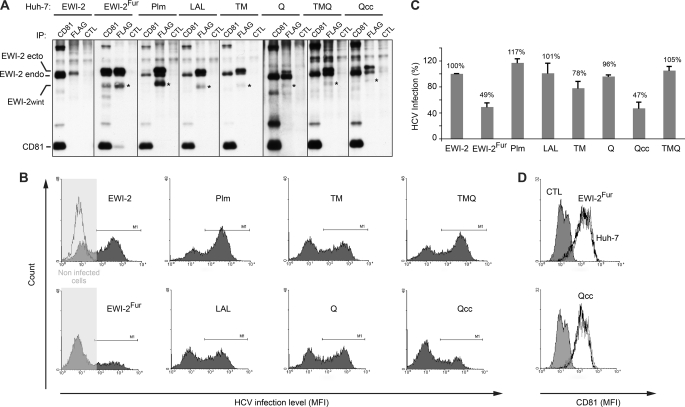
FIGURE 6.
Mutations in EWI-2/EWI-2wint that abolish interaction with CD81 also affect the inhibitory effect of EWI-2wint on HCV infection. A, Huh-7 cell clones expressing the different FLAG-tagged mutants of EWI-2/EWI-2wint were biotinylated, lysed in PBS/Brij97/EDTA, immunoprecipitated, and detected using HRP-streptavidin. CD81 and FLAG IP were performed with 5A6 and M2 mAbs, respectively. CTL IP were performed with irrelevant immunoglobulins. Endogenous (EWI-2 endo) and ectopic (EWI-2 ecto) EWI-2 proteins are indicated. Asterisks show bands corresponding to EWI-2wint protein. B and C, HCVcc infection levels in Huh-7 cells expressing EWI-2/EWI-2wint proteins. Infected cells were stained using anti-NS5 mAb (2F6/G11) and secondary antibodies were conjugated with PE. Noninfected cells were used as negative controls. A representative histogram of every clone is shown in B. Histograms are characterized by two peaks, one corresponding to the noninfected cells (left) and the other corresponding to the infected cells (right). In C, results are presented as relative percentages to full-length EWI-2 expressing cells and reported as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. D, CD81 expression on cells expressing EWI-2Fur or Qcc proteins. Cells were stained using 5A6 and secondary antibodies conjugated with PE. CTL corresponds to cells that were stained only with secondary antibodies. CD81 expression on cells expressing EWI-2Fur or Qcc EWI-2/EWI-2wint proteins (black line) was compared with that of parental Huh-7 cells (gray line).