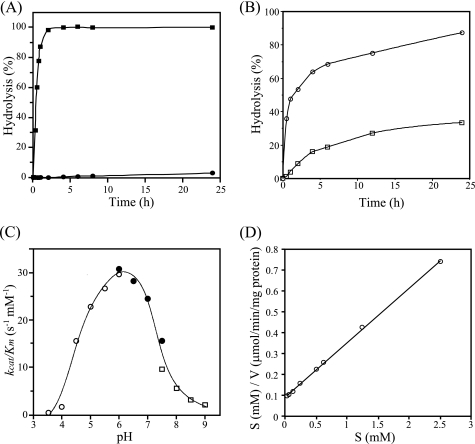
FIGURE 2.
Specificity and general properties of NgaP. A, time course for the hydrolysis of pNP-β-HexNAc by NgaP. Aliquots of 50 nmol of pNP-β-GalNAc (■) and pNP-β-GlcNAc (●) were incubated with 1 milliunit of the enzyme at 37 °C for the periods indicated in 100 μl of 25 mm acetate buffer (pH 6.0). The hydrolysis of pNP-substrates was examined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, time course of the hydrolysis of GSLs by NgaP. Aliquots of 5 nmol of GA2 (○) and Gb4Cer (□) were incubated with 10 milliunits of the enzyme at 37 °C for the times indicated in 20 μl of 25 mm acetate buffer (pH 6.0). The hydrolysis of GSLs was examined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, pH-kcat/Km profile of wild-type NgaP. The reaction mixture containing different amounts of pNP-β-GalNAc (12.5–200 nmol) and an appropriate amount of enzyme in 100 μl of various buffers (25 mm) was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. ○, acetate buffer (pH 3.5–6.0); ●, phosphate buffer (pH 6.0–7.5); □, Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5–9.0). The kcat/Km values were determined using the Hanes-Woolf plot. D, Hanes-Woolf plot for the action of NgaP. The concentration of pNP-β-GalNAc was varied as indicated, and the incubation time was 30 min. Values are means of triplicate determinations.