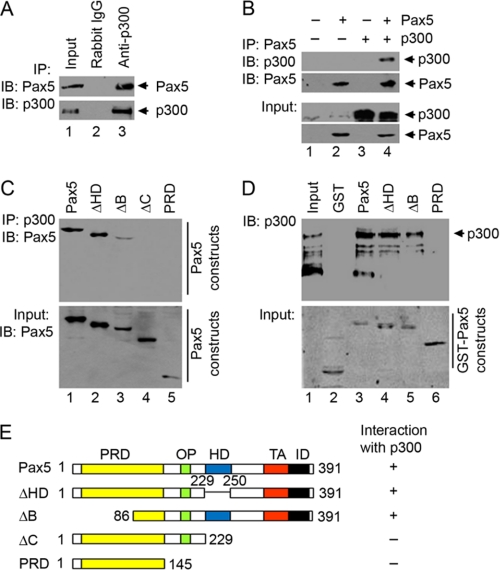
FIGURE 2.
Pax5 interacts with p300. A, immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using nuclear proteins extracted from human B lineage EU12 cells with non-relevant control rabbit IgG or anti-p300 antibodies. Input (10% of sample) or immunoprecipitated samples were analyzed by Western blotting (IB) using mouse monoclonal anti-Pax5 antibodies or rabbit polyclonal anti-p300 antibodies. B, immunoprecipitation was performed using nuclear proteins extracted from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with different combinations of Pax5 and p300 expression vectors. Immunoprecipitated samples were analyzed by Western blotting using monoclonal anti-Pax5 antibodies or rabbit polyclonal anti-p300 antibodies. The expression levels of Pax5 and p300 in the nuclear extracts were also analyzed by Western blotting and shown as Input. C, interaction of p300 with different Pax5 constructs. Nuclear extracts were prepared from HEK293 cells co-expressing p300 with different Pax5 constructs and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-p300 antibodies. Immunoprecipitated samples were analyzed by Western blotting using goat polyclonal anti-Pax5 antibodies N-19 and C-20 or rabbit polyclonal anti-p300 antibodies. The expression of different Pax5 constructs was also analyzed by Western blot and shown as input. D, different GST fusion Pax5 constructs were expressed and purified from HEK293 cells with or without co-expression of p300 and retained on the glutathione-agarose beads for interaction with purified recombinant p300 protein. Bound p300 proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by rabbit polyclonal anti-p300 antibodies. Different purified GST-Pax5 truncations were detected by Coomassie Blue staining (shown as Input). E, diagrams of different Pax5 constructs with functional domains. Their abilities to interact with p300 are summarized. PRD, paired box DNA binding domain; OP, Oct-peptide; HD, homeolike domain; TA, transactivation domain; ID, inhibition domain.