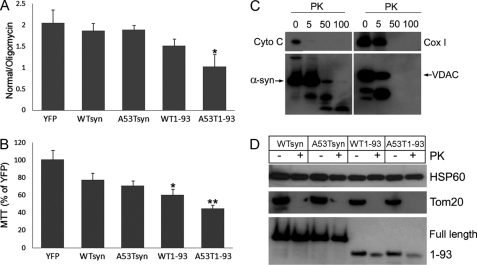
FIGURE 6.
Localization of α-synucleins into the mitochondrial matrix and significant decrease in mitochondrial O2 consumption and survival by A53T1–93. Tetracycline-inducible 293 cells expressing various α-synuclein constructs, including full-length WT and A53T, 1–93-amino acid WT, and A53T (WTsyn, A53Tsyn, WT1–93, and A53T1–93, respectively), were incubated with tetracycline for 5 days. Tetracycline-inducible 293 cells overexpressing YFP were used as a control. A, mitochondrial O2 consumption was measured. n = 5. B, cell survival was measured using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay after culture in galactose media for 1 week. n = 5. C, mitochondrial fractions of cells overexpressing A53Tsyn were treated with various concentrations of proteinase K (PK) (0–100 μg/ml). Degradation of submitochondrial marker proteins and α-synuclein were detected by specific antibodies: Cyto C, cytochrome c (intermembranous space); α-syn, anti-FLAG antibody; VDAC (voltage-dependent anion channel) (outer membrane); Cox1 (inner membrane). D, after incubation of mitochondrial fractions with 5 μg/ml PK for 30, degradation of submitochondrial marker proteins and α-synuclein was detected by anti-Hsp60 antibody for matrix protein, anti-Tom20 antibody for outer membrane protei, and anti-FLAG antibody for α-synuclein. Data are shown as the mean ± S.D. Statistical analysis was performed using the Student t test. *, p < 0.05 versus YFP; **, p < 0.01 versus YFP.