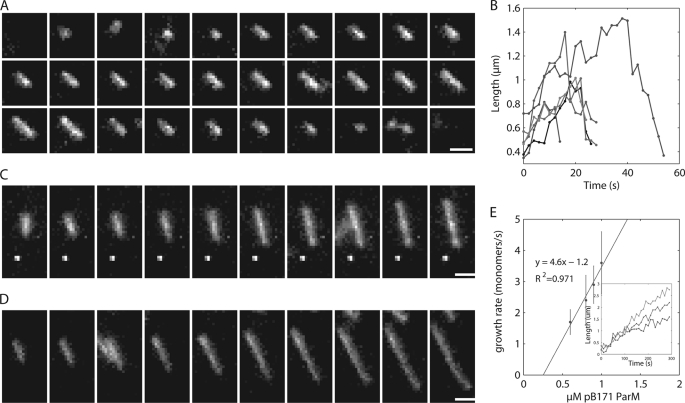
FIGURE 6.
Time-lapse TIRF microscopy observing individual filaments demonstrate that pB171 ParM is dynamically unstable when polymerized in ATP and appears to elongate symmetrically. A, montage of an individual pB171 ParM filament in ATP. 25% Alexa 488-labeled 2.8 μm B171 ParM was polymerized in the presence of 10 mm ATP and imaged via TIRF microscopy every 2 s. Buffer conditions were as follows: 100 mm KCl, 30 mm KCl, 1 mm MgCl2, 1 mm DTT, 0.8% methylcellulose, 0.5% BSA. Scale bar, 1 μm. B, length versus time for six representative filaments polymerized in ATP. C and D, montage of individual filaments polymerized in nonhydrolyzable AMP-PNP. 25% Alexa 488-labeled 0.8 μm or 1.0 μm pB171 ParM was polymerized in the presence of 10 mm AMP-PNP. The time interval is 20 s between each frame. Buffer conditions are the same as in ATP. Scale bar, 1 μm. E, rate of elongation of AMP-ParM. The rate of elongation was measured at various concentrations of pB171 ParM in AMP-PNP and plotted versus the μm pB171 ParM. The line fit to the data represents the equation: rate of filament elongation = kon x (μm protein)-koff. Inset shows three representative filaments growth over time from 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 μm pB171 concentrations.