Figure 2.
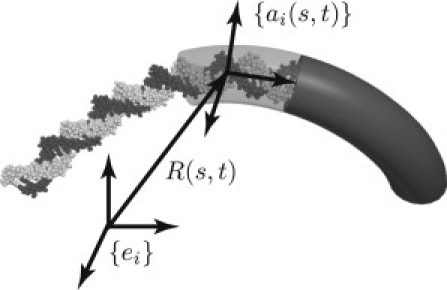
The all-atom structure of DNA is approximated by an elastic rod with equivalent (averaged) elastic properties. The position vector R(s,t) locates the helical axis of DNA as a function of the contour length coordinate s and time t with respect to the inertial frame {ei}. Similarly, {ai(s,t)} describes a body-fixed frame of a cross section of the rod as a function of s and t. Figure modified from Lillian et al. (32).
