Figure 5.
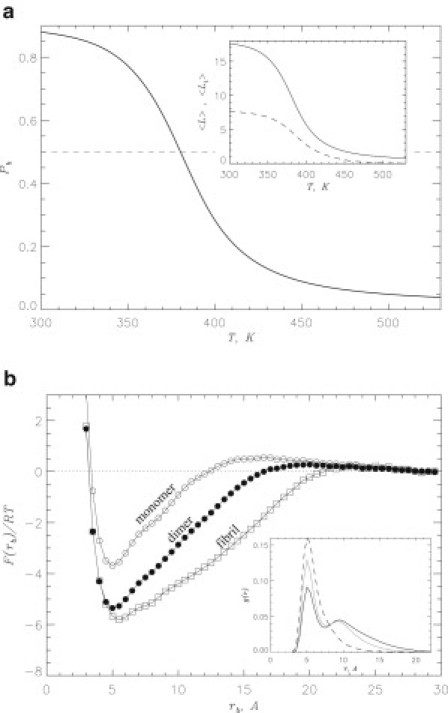
(a) Probability of naproxen molecule binding to Aβ dimer, , as a function of temperature. Binding temperature Tb is associated with the midpoint of . Inset shows the number of naproxen ligands bound to Aβ dimer (continuous line) and the number of ligands bound to Aβ aggregation interface (dashed line) versus temperature. (b) Free energy of naproxen as a function of the distance between ligand and Aβ dimer, rb (solid circles). The free energy of binding is computed by integrating over the ligand bound states with , where Fmin is the minimum in . The values of F at Å are set to zero and correspond to unbound state. Free energies describing naproxen binding to Aβ monomer and fibril computed earlier (35) are given by open circles and squares, respectively. Inset: Radial distribution functions, and , map minimum distances between amino acids from different peptides and between ligands and amino acids, respectively. The functions obtained in water and naproxen solution are shown by continuous gray and black lines; the function is represented by a dashed line. All plots in (b) are obtained at 360 K. The figure implies that naproxen binds to Aβ dimer and interferes with interpeptide interactions.
