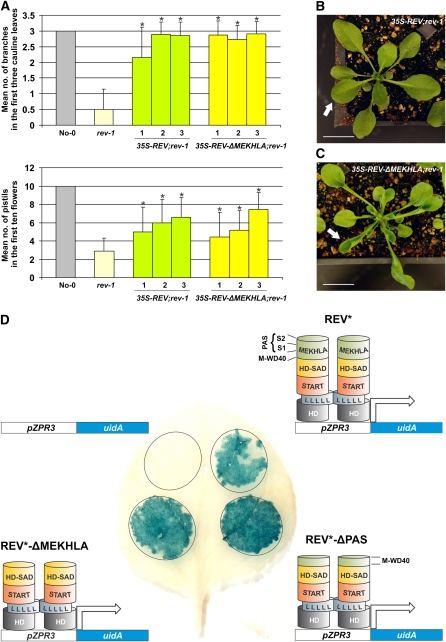
Figure 2.
The REV MEKHLA Domain Is Not Necessary for REV Activity in Vivo.
(A) Arabidopsis rev-1 plants were transformed with 35S-REV or 35S-REV-ΔMEKHLA constructs. Three independent T2 lines (1 to 3) for each genotype were examined for the number of branches in the first three cauline leaves and for the number of pistils in the first 10 flowers. rev-1 and wild-type plants (No-0) were also analyzed as controls. Standard deviations (error bars) were calculated from more than 30 individuals. Asterisks indicate transgenic lines that are statistically different from rev-1 (Student's t test, P < 0.05). A combined analysis of the lines 1 to 3 of 35S-REV; rev-1 and 35S-REV-ΔMEKHLA; rev-1 plants shows no statistically significant difference (Student’s t test, P > 0.05) in the number of pistils and a mild difference (Student’s t test, P = 0.026) in the number of branches. Lines 2 and 3 have no statistically significant difference (Student's t test, P > 0.05) in the number of branches.
(B) A representative individual (6 weeks old) of 35S-REV; rev-1 transgenic plants. The white arrow points to a normally flattened leaf. Bar = 100 mm.
(C) A representative individual (6 weeks old) of 35S-REV-ΔMEKHLA; rev-1 transgenic plants. The white arrow points to an abnormally curled up leaf. Bar = 100 mm.
(D) β-Glucuronidase expression in leaf abaxial (lower) epidermal cells of tobacco transiently transformed with pZPR3-uidA and 35S (empty vector), pZPR3-uidA, and 35S-REV*, pZPR3-uidA, and 35S-REV*-ΔPAS, or pZPR3-uidA and 35S-REV*-ΔMEKHLA constructs. miRNA-resistant REV is designated REV*. REV homodimerization through the leucine zipper domain is schematically represented by two strings of Leu residues (L) touching each other.