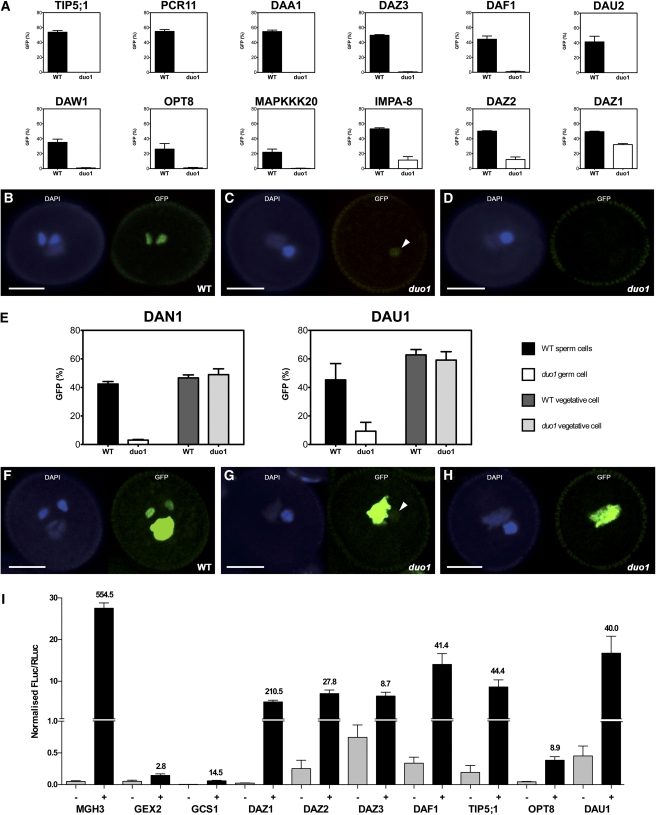
Figure 2.
A Selection of Induced Target Genes Exhibit DUO1-Dependent Expression in the Male Germline.
(A) Promoter activity of male germline-specific DAT genes. GFP expression was scored in single insert hemizygous lines in the duo1-1/+ background. Wild-type (WT) pollen grains (black) were distinguished from duo1 pollen grains (white) by germ cell number. Each bar represents the mean of at least three independent lines and error bars represent the se. All 12 promoters show significantly reduced activity in duo1 germ cells compared with wild-type sperm cells (two-tailed χ2 test: P < 0.0001).
(B) to (D) Examples of male germline-specific DAT gene promoter activity in wild-type and duo1 pollen using CLSM. Each panel shows a representative pollen grain under DAPI fluorescence (left) and GFP fluorescence (right). Sperm cell nuclei in wild-type pollen grains show a GFP signal (B), while duo1 germ cell nuclei show a residual level (C) or no detectable GFP signal (D). Arrowheads indicate a residual level of GFP signal in duo1 germ cells. Bars = 10 μm.
(E) Promoter activity of DAT genes expressed in the vegetative and sperm cells. GFP expression was scored in single insert hemizygous lines in the duo1-1/+ background for wild-type sperm cells (black), wild-type vegetative nuclei (dark gray), duo1 germ cells (white), and duo1 vegetative nuclei (light gray). Each bar chart represents the mean of at least three independent lines, and error bars show the se. The two promoters show significantly reduced activity in duo1 germ cells compared with wild-type sperm cells (two-tailed χ2 test: P < 0.0001), but there is no significant difference between activity in the vegetative cells.
(F) to (H) Examples of non-male germline-specific DAT gene promoter activity in wild-type and duo1 pollen grains using CLSM. Each panel shows a representative pollen grain under DAPI fluorescence (left) and GFP fluorescence (right). Both sperm cell and vegetative cell nuclei in wild-type pollen grains show a GFP signal (F), while duo1 germ cell nuclei either show a residual level (G) or no detectable GFP signal (H), and the GFP signal of vegetative cell nuclei is unaffected in duo1 pollen grains ([G] and [H]). Arrowheads indicate a residual level of GFP signal in duo1 germ cells. Bars = 10 μm.
(I) DUO1-dependent transactivation of validated DAT promoters in tobacco leaves. The relative luciferase activity (FLuc/RLuc) of each target promoter (ProDAT:LUC) alone (−; light gray) and upon coinfiltration with Pro35S:mDUO1 (+; dark gray) is shown with the fold change indicated above the (+) column. Each bar represents the mean of at least four independent infiltrations, and error bars show the se. A split y axis is presented in order to illustrate lower level activity.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]