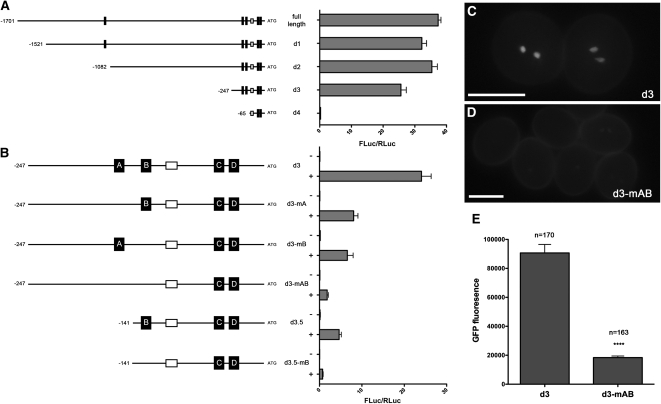
Figure 4.
MYB Binding Sites Are Critical for DUO1-Dependent Transactivation of the MGH3 Promoter.
(A) Relative luciferase activity of 5′ deletions in the MGH3 promoter. Left shows the promoter sequences highlighting MYB sites (black boxes) and the canonical TATA box (white box). Right shows the mean relative luciferase activity (FLuc/RLuc) for at least four independent infiltrations, and error bars show the se.
(B) The significance of MYB sites for DUO1-dependent transactivation of the MGH3 promoter. Left shows the promoter fragments with targeted mutations and/or deletions in context of d3 of the MGH3 promoter with MYB sites named A to D. Right shows the mean FLuc/RLuc for at least four independent infiltrations, and error bars show the se.
(C) Example of ProMGH3d3:H2B-GFP activity in mature pollen. Bar = 15 μm.
(D) Example of ProMGH3d3_mAB:H2B-GFP activity in mature pollen. A clear decrease in GFP signal was observed in several independent lines. Error bars represent the se. Bar = 15 μm.
(E) The decrease in GFP signal observed in ProMGH3d3_mAB:H2B-GFP lines. GFP fluorescence represents the mean total pixel intensity corrected for background in (n) sperm cells analyzed. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences determined using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test (P < 0.0001, U = 2768).