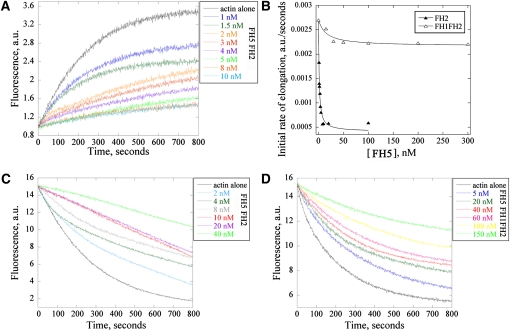
Figure 7.
FH5 Binds to the Barbed End of Actin Filaments and Inhibits Dilution-Mediated Actin Depolymerization.
(A) Kinetics of actin filament barbed end elongation. Preformed actin filaments (1.0 μM) were incubated with various concentrations of FH5 FH2 before the addition of 0.4 μM pyrene-labeled actin monomers. a.u., absorbance units.
(B) Plot of the initial rate of actin elongation versus the concentrations of FH5 FH2 and FH5 FH1FH2. The equilibrium dissociation constant was calculated by fitting the data with Equation 1 (see Methods). The representative Kd is 1.2 nM for FH5 FH2 and 14.6 nM for FH5 FH1FH2.
(C) and (D) Kinetics of actin depolymerization in the presence of various concentrations of FH5 FH2 (C) and FH5 FH1FH2 (D) monitored by the decrease in pyrene fluorescence. F-actin (5 μM) was incubated with various concentrations of FH5 FH2 or FH5 FH1FH2 for 5 min at room temperature, and actin depolymerization was initiated by diluting the mixtures 25-fold into buffer G.