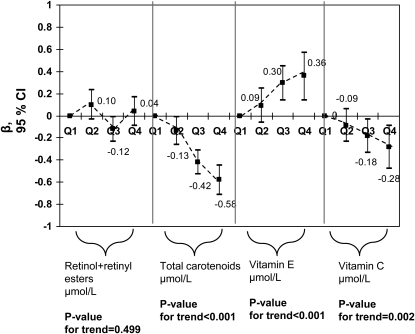
FIGURE 1.
Major serum antioxidant concentrations by quartiles (Q2, Q3, Q4 vs. Q1) and MetS (NCEP ATP III definition) score count outcome among U.S. adults (NHANES 2003–2006); n = 1,574. Values are adjusted β (95% CI). Ranges for each antioxidant quartile is as follows in μmol/L: retinol+retinyl esters (Q1: 0.066–1.703; Q2: 1.703–2.083; Q3: 2.084–2.521; Q4: 2.522–8.860); total carotenoids (Q1: 0.057–0.863; Q2: 0.863–1.183; Q3: 1.183–1.622; Q4: 1.62–10.114); vitamin E (Q1: 0.16–21.66; Q2: 21.67–27.35; Q3: 27.37–35.94; Q4: 35.95–303.81); and vitamin C (Q1: 0.6–34.6; Q2: 35.2–54.5; Q3: 55.1–70.4; Q4: 71.0–274.2). Analyses were based on multiple ZIP regression models that simultaneously included all antioxidant exposures and adjusted for socio-demographic factors: age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, educational level, and PIR and other potential confounders, including: lifestyle and health-related factors (smoking status, PA: Met⋅h⋅wk−1, recoded as 0 to <5, 5–10, >10) and dietary intakes (total energy intake, alcohol, caffeine, β-carotene, vitamin C, vitamin E, and dietary supplement use), serum levels of folate, tHcy, vitamin B-12, 25(OH)D, total cholesterol, and TG.