Fig. 5.
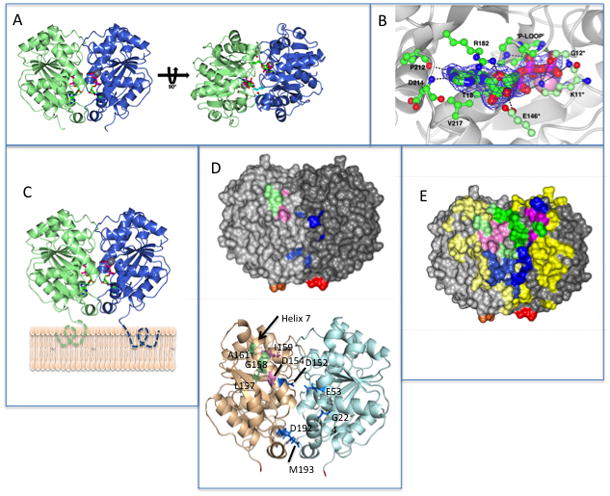
The dimeric structure of MinD and the location of residues involved in MinD and MinE binding. (A) Each monomer is colored differently and the ATPs (stick diagram) and Mg ions (gray spheres) are indicated. In the structure on the right the side chains for lysine 11, which reach across the dimer interface, are depicted.
(B) Residues interacting with ATP. Residues on one subunit important for ATP binding are indicated by a darker shade of green. The three residues making contact with ATP across the dimer interface (G12 and E146 in addition to K11) are indicated with an * and are a lighter shade of green. (C) Model of MinD bound to the membrane. The residues missing from the structure (KKGFLKRLFGG) that the form an an amphipathic helix involved in membrane binding are indicated by dotted lines extending from C-terminus of MinD. The orientation of MinD is the same as the structure on the left in panel A. (D) Location of the 4 residues identified in the random screen that are important for MinE interaction, but not for MinC, (E53, D192, M193 and G224; indicated in blue) relative to previously identified residues important for MinE or MinC binding. Based upon the model in panel (C) these residues are closer to the membrane. The location of D152 (blue), D154 and I159 (pink; involved in both MinC and MinE interaction) and L157, G158 and A161 (green; specifically required for MinC interaction) are also indicated. The C-terminal glutamate residues present in the structure are colored red and orange. The orientation of MinD is the same as in panel C.
(E) Location of MinD residues involved in interaction with MinE and MinC. The structure is of the MinD (same orientation as panel C) dimer with residues colored as in D. For all residues the lighter shade is the monomer to the left and the darker shade is the monomer to the right. Residues not involved in binding MinC or MinE are colored yellow. Three types of residues important for binding are indicated. Those specifically involved in MinE binding are blue, those specifically involved in MinC binding are green and those involved in both MinC and MinE binding are pink. The C-terminal glutamates are colored red and orange.
