Figure 4. The bortezomib-induced nuclear translocation of IκBα results in the suppression of NFκB DNA binding activity and induction of apoptosis in Hut-78 cells.
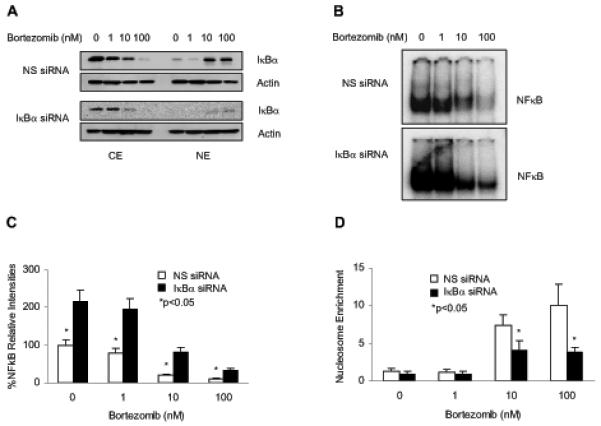
(A) Western blotting of CE and NE prepared from Hut-78 cells transfected with non-silencing (NS) or IκBα siRNA, followed by treatment with increasing concentrations of bortezomib for 24 h. The membranes were analyzed by using IκBα and actin antibodies. (B) Representative EMSA assay of NFκB DNA binding activity measured in Hut-78 cells transfected with NS (top panel) or IκBα (bottom panel) siRNA, followed by incubations with increasing concentrations of bortezomib for 24 h. (C) Densitometric evaluation of the EMSA assays of NFκB DNA binding activity measured in Hut-78 cells transfected with NS (empty columns) or IκBα (full columns) siRNA as described above in Fig. 4B. (D) Apoptosis measured by the nucleosome enrichment assay in Hut-78 cells transfected with NS (empty columns) or IκBα (full columns) siRNA, followed by 24 h treatment with increasing concentrations of bortezomib. The values shown in panels (C) and (D) represent the mean +/−SE of four experiments; asterisks denote a statistically significant (p<0.05) change compared to control si RNA transfected cells.
