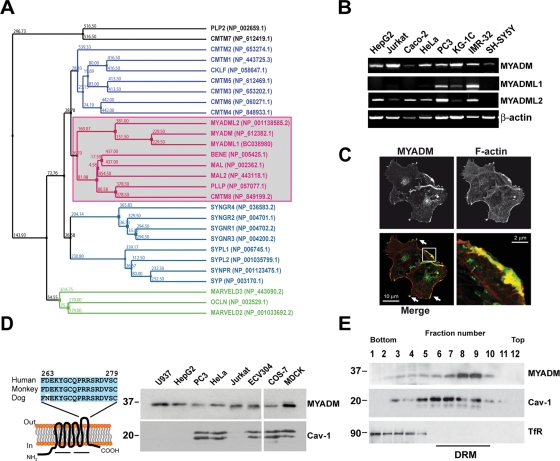
FIGURE 1:
Characterization of the MYADM protein and analysis of its subcellular distribution. (A) Complete phylogenetic tree of human MARVEL domain-containing proteins. The sequences of the cytoplasmic amino- and carboxyl-terminal tails were not considered in the alignment used to generate the tree. The protein accession numbers of the corresponding sequences are indicated in brackets; the nucleotide accession number is indicated in the case of MYADML1. The MAL protein family is boxed. (B) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the MYADM, MYADML1, and MYADML2 genes in various human cell lines. (C) Cos-7 cells expressing human MYADM-GFP were stained for F-actin and analyzed by confocal microscopy. The enlargement shows the colocalization of MYADM and F-actin in the lamellipodia indicated in the boxed area. (D) Left panel: schematic model of the predicted structure of MYADM indicating the human peptide used for the generation of mAb2B12. The two lines below the model indicate the two MARVEL domains present in the MYADM molecule. Right panel: total membrane fractions from the indicated cell lines were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-MYADM mAb 2B12 or anti-caveolin-1 (Cav-1) antibodies. (E) HeLa cells were extracted with 1% Triton X-100 at 4ºC and centrifuged to equilibrium in sucrose-density gradients. Aliquots from each fraction were immunoblotted for MYADM with 2B12 mAb or for caveolin-1 (Cav-1) and TfR used as markers of the DRM and soluble fractions, respectively.