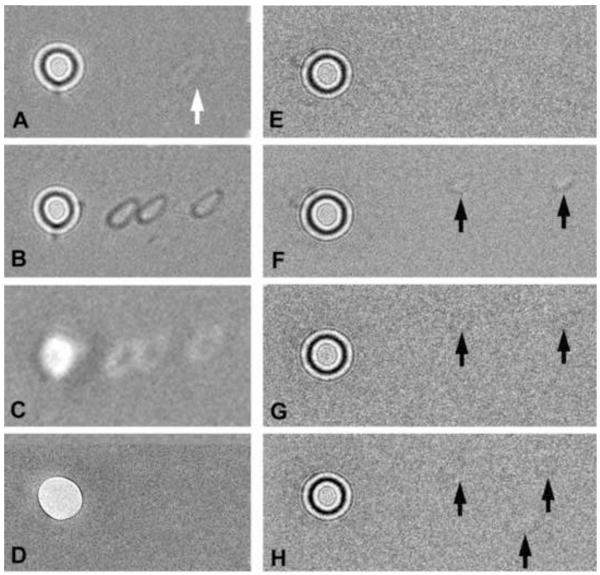
Figure 6.
Testing charge of phase-plate carbon films. Appearance of two phase plates (A-D and E-H) after spot-irradiation of the carbon film adjacent to the central hole. No specimen is inserted, and the condenser lens is set for the on-plane condition, with a total beam current of 1 nA. After spot irradiation, the condenser is overfocused, and images are recorded with an electron dose of 0.24 e−/nm2 on the carbon film. (A) Phase plate after spot-irradiation (at arrow) with 3 × 106 e−/nm2. This corresponds to an incident electron dose on the specimen (if it were present) of 150 e−/nm2. The faint white footprint indicates neutralization of positive charge on the carbon film, as typified by the Berriman effect. Note that the beam footprint, while small enough to pass the central hole, is not round (due to slight condenser-lens astigmatism), in spite of the fact that the illumination appeared circular at the specimen plane. (B,C) Demonstration of contrast reversal when the condenser lens is underfocused with respect to the on-plane condition. (D) In-focus image of the phase plate taken in the “low-mag” mode, focused by the objective minilens. The footprints are not visible, indicating that they are not due to appreciable contamination (which would be detectable by amplitude contrast). (E) Phase plate before spot irradiation. (F) Two footprints (arrows) created from individual spot exposures of 6 × 106 e−/nm2. Image recorded with double intensity to make the footprints more visible. (G) Image of phase plate after the entire phase plate was illuminated with a strong beam for 15 min (total dose 2.8 × 1015 e−/μm2). The footprints are nearly erased due to a charge neutralization effect and/or etching of most of the insulating contamination on the phase plate. (H) A third, slightly larger, footprint was created (lower arrow). Since the phase plate is now less-charged, the new footprint is fainter than in (F). The amount of charging of both of these phase plates was not excessive for medium-resolution imaging, and they yielded images with good phase contrast.