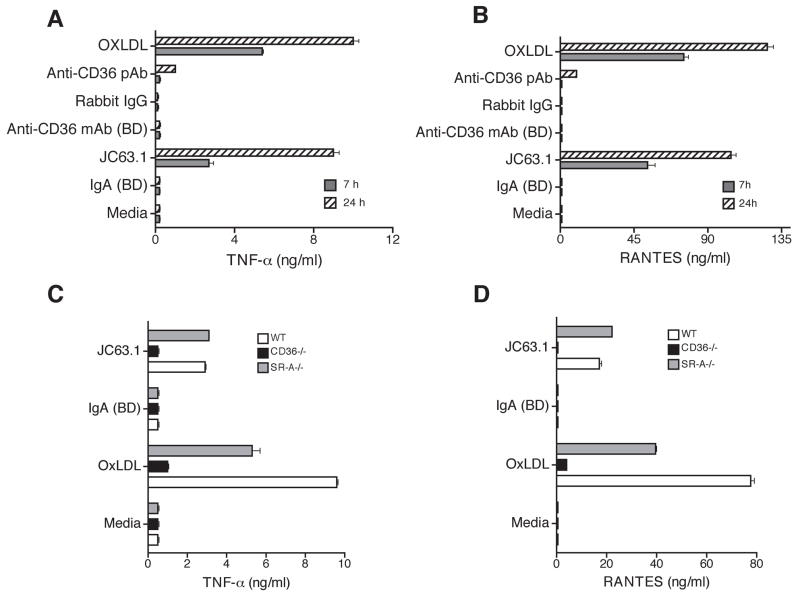
Figure 2. Activating mouse CD36 mAb induces inflammatory cytokine response in primary macrophages is dependent on CD36 expression.
Thioglycollate-elicited apoE−/− peritoneal macrophages were treated with indicated mouse anti-CD36 antibodies including the activating mCD36 mAb (JC63.1). Cells treated with mIgA, rabbit IgG, or oxLDL were used as controls. Supernatant collected after 7 or 24 h was used to determine TNF-α (A) and RANTES (B) secretion. Peritoneal macrophages collected from wild type (apoE−/−), CD36−/− (apoE−/−CD36−/− double deficient), and SRA−/− (apoE−/−SR-A−/− double deficient) were treated the activating mCD36 mAb. After 18 h, supernatant was collected and TNF-α (C) and RANTES (D) secretion were determined. Macrophages incubated with oxLDL and mIgA were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Data are representative of three independent experiments.