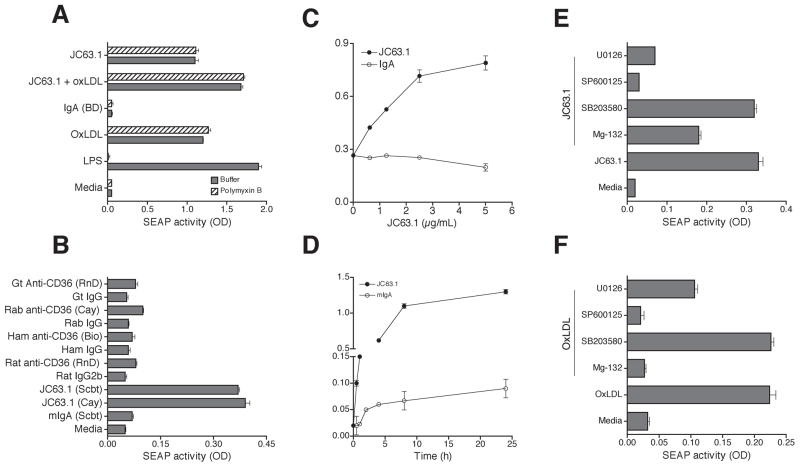
Figure 4. Activating mCD36 mAb-induced inflammatory cytokine response is dependent on NF-κB and MAP kinase activation.
To address signaling pathways regulating the inflammatory cytokine response initiated by the activating mCD36 mAb, RAW-Blue-SEAP reporter cells were used. RAW-Blue cells were pretreated with activating mCD36 mAb or other indicated reagents. Supernatant collected after 18 h was analyzed for SEAP reporter activity (A). RAW-Blue cells were incubated for 18 h with the activating mCD36 mAb or other anti-mCD36 mAb or pAb to determine the specificity of activating mCD36 mAb induced NF-κB and AP-1 activation (B). Cells treated with mIgA or cultured in medium were used as controls. RAW-Blue cells were treated with activating mCD36 mAb at different concentration (C) or different incubation time (D) to determine the dose-dependent and kinetics of macrophage activation. RAW-Blue cells were treated with activating mCD36 mAb (E) or oxLDL (F) in the absence or presence of Mg-132 (NF-κB inhibitor), SB203580 (p38 inhibitor), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), or U0126 (Erk1/2 inhibitor). Cells cultured in media alone served as the control. Data are Mean ± SD of triplicates and representative of two independent experiments is presented.