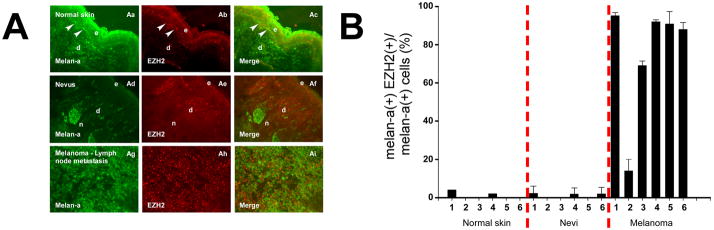
Figure 1.
Expression of EZH2 in skin, melanocytic nevi, and metastatic melanomas. (A) In vivo melanocytic expression of EZH2. Aa–Ac depict expression of Melan-a (Aa), EZH2 (Ab), and merged image (Ac) in normal human skin. Arrowheads point to Melan-a-expressing melanocytes in basal layer (Aa), which do not express EZH2 (Ab). Epidermis (e) and dermis (d) are delineated. Ad–Af show expression of Melan-a (Ad), EZH2 (Ae), and merged image (Af) in an example of a compound melanocytic nevus Nests (n) of adherent nevus cells in the dermis are depicted. EZH2 expression is absent in these and in individual melanocytes (Ae). Ag–Ai demonstrate expression of Melan-a (Ag), EZH2 (Ah) in tissue from a melanoma lymph node metastasis. Merged image (Ai) shows that most cells express both Melan-a and EZH2. (B) Proportions of Melan-a-expressing cells in normal human skin, melanocytic nevi, and metastatic melanomas that express EZH2. Nevi and melanoma specimens correspond to specimens presented in Figure 1A (#1) and to specimens presented sequentially (#2–6) in Supplementary Figures 1 and 2. Error bars represent standard deviations from the mean.