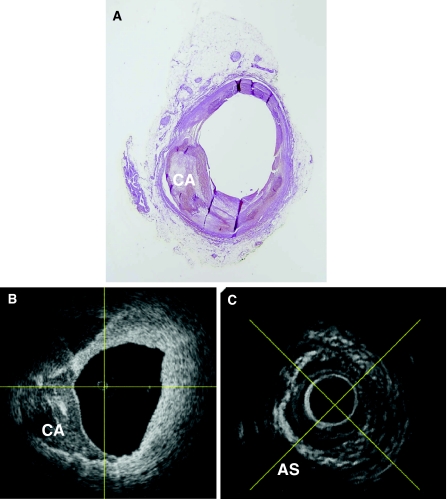
Fig. 2.
One of the main limitations of processing the RAW radiofrequency data only, not taking into account other information available, such as visible acoustic shadowing, is that these signal processing methods identify tissue components in these acoustic shadowed regions while IVUS does not return any information about it. The ultrasound waves are reflected at the calcium interface as can be appreciated in this figure. A presents a histology sample of an explanted human coronary artery of which in B the OCT image is presented and in C the IVUS equivalent. It can be appreciated that OCT presents the calcium very well between 6 and almost 12 o’clock. Also within the IVUS image it can be appreciated that between 6 and 12 o’clock there is a calcium layer present due to the white and bright interface but everything behind it is shadowed and thus IVUS does not contain any information deeper than this interface. When using IVUS as the only source to estimate the plaque composition tissue within these shadowed areas should therefore be classified as unknown tissue