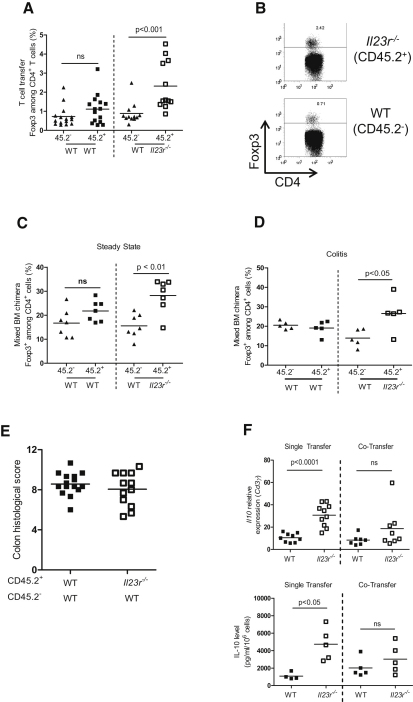
Figure 6.
IL-23 Inhibits Intestinal iTreg Cell Generation via a Direct Cell-Intrinsic Mechanism
(A and B) C57BL.6.Rag1−/− mice were transferred with 1:1 mixtures of CD45.2− (WT) + CD45.2+ (WT) or CD45.2− (WT) + CD45.2+(Il23r−/−) CD4+CD45RBhi T cells. Mice were sacrificed upon development of clinical signs of inflammation (∼8 weeks).
(A) The frequency of Foxp3+ cells among T cells in the colon was assessed by intracellular flow cytometry.
(B) Representative FACS plots showing Foxp3 expression in CD4+ T cells in the colon; numbers in quadrants represent frequencies. Data represent pooled results from two independent experiments, n = 15 (WT + WT), n = 12 (WT + Il23r−/−).
(C and D) Sublethally irradiated C57BL.6.Rag1−/− mice were reconstituted with 1:1 mixtures of CD45.2− (WT) + CD45.2+ (WT) or CD45.2− (WT) + CD45.2+(Il23r−/−) bone marrow cells. The frequency of Foxp3+ cells among CD4+ cells in the colon was assessed by intracellular FACS during steady state (C) or during colitis induced by infection with Helicobacter hepaticus plus treatment with a blocking IL-10R mAb (D). Data represent results from a single experiment; n = 5–7 (WT + WT), n = 5–7 (WT + Il23r−/− T cells).
(E) Colitis scores from mice in (A); data represent pooled results from two independent experiments.
(F) Il10 mRNA levels and protein levels in supernatants after restimulation of CD4+ T cells purified from the colons of C57BL.6.Rag1−/− mice transferred with WT or Il23r−/− CD4+CD45RBhi T cells as described in Figure 1 (single transfer) or from recipients of 1:1 mixtures of WT + Il23r−/− CD4+CD45RBhi T cells as described above (cotransfer). Data represent pooled results from two independent experiments (top, n = 7–10 per group) or from a single experiment (bottom, n = 5 per group).
Bars represent the mean; each symbol represents an individual mouse; statistical significance was determined with the Mann-Whitney test.