Figure 8.
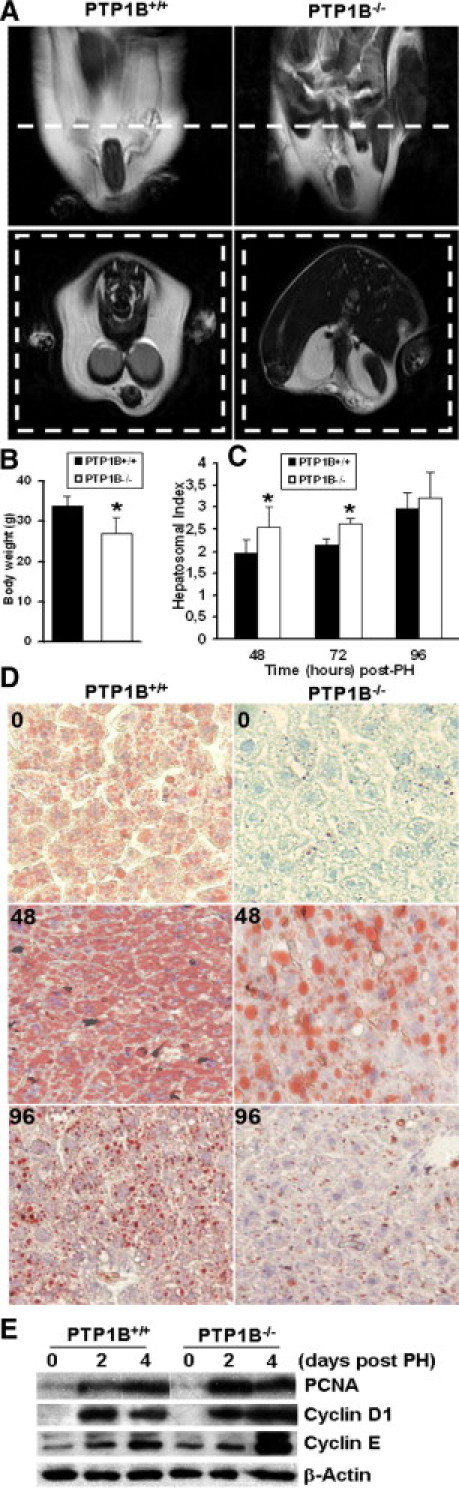
The PTP1B deficiency protects from diet-induced steatosis and improves hepatic regeneration under HFD conditions. A: Comparison of visceral fat mass in PTP1B+/+ and PTP1B−/− mice fed an HFD for 12 weeks after weaning. Animals were subjected to RMN scan analysis in fed conditions. The images were acquired in axial or coronal orientation. B: Comparison of total body weight in PTP1B+/+ and PTP1B−/− mice fed an HFD for 12 weeks after weaning. Results are given as the mean ± SEM (n = 8). *P < 0.05 for PTP1B−/− versus PTP1B+/+ mice. C: The PH was performed in PTP1B+/+ and PTP1B−/− mice after 12 weeks of an HFD, and regenerating livers were removed at the indicated periods. The liver regeneration index (liver/body weight ratio) is given after PH. Results are given as the mean ± SEM (n = 8). *P < 0.05 for PTP1B−/− versus PTP1B+/+ mice. D: Oil red O staining of liver sections from PTP1B−/− and PTP1B+/+ mice after 12 weeks of HFD and at 48 to 96 hours after PH. Original magnification, ×10. E: Representative Western blot analysis with the antibodies against PCNA, cyclins D1 and E, and β-actin as a loading control.
