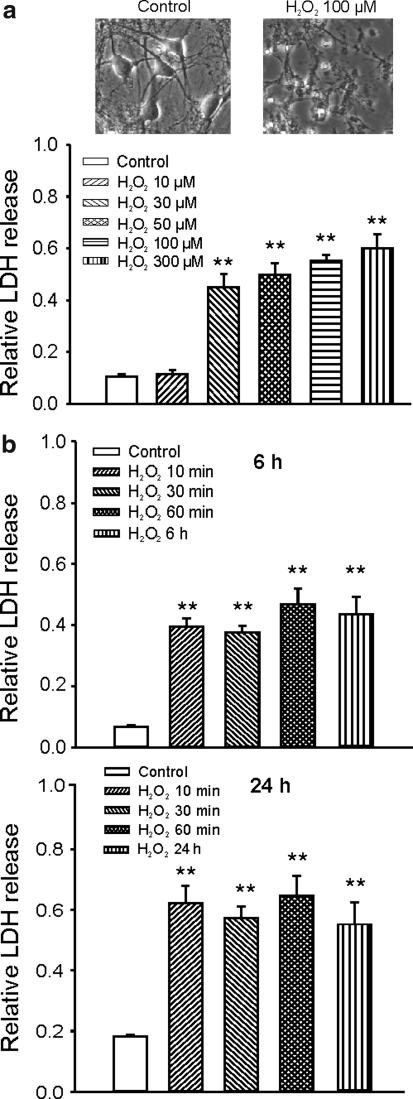
FIG. 1.
Concentration- and duration-dependent neuronal injury induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of blockers of glutamate receptors and L-type Ca2+ channels. (a) Example phase-contrast images showing neurons before or 24 h after incubation with 100 μM H2O2 (upper panels) and summary bar graph showing concentration-dependent neuronal injury by H2O2 (lower panel). Cultured mouse cortical neurons grown in 24-well plates were treated with different concentration of H2O2 for 1 h in the presence of 10 μM (5R,10S)-(+)-5-Methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine (MK801), 20 μM 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX), and 5 μM nimodipine. Neuronal injury was assayed by measurement of the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released into the culture medium at 24 h after the H2O2 exposure. The relative LDH release was calculated by normalizing the amount of LDH released at 24 h to the maximal releasable amount of LDH induced by permeabilizing cells with 1% triton X-100. The relative LDH release for control, 10, 30, 50, 100, and 300 μM H2O2 was 0.11 ± 0.01, 0.11 ± 0.02, 0.45 ± 0.05, 0.5 ± 0.05, 0.55 ± 0.02, and 0.60 ± 0.05, respectively (n = 7–8). (b) Summary data demonstrating duration-dependent neuronal injury by 100 μM H2O2. Neurons were treated with 100 μM H2O2 in the presence of MK801, CNQX, and nimodipine for 10 min, 30 min, 60 min, and continuous treatment. Relative LDH release was measured at 6 or 24 h after H2O2 exposure. At 6 h after the exposure of H2O2 for 0 min, 10 min, 30 min, 60 min, and 6 h (continuous), relative LDH release was 0.07 ± 0.01, 0.40 ± 0.03, 0.38 ± 0.02, 0.49 ± 0.06, 0.35 ± 0.05, and 0.46 ± 0.06 (n = 4 wells each). At 24 h after the exposure of H2O2 for 0 min, 10 min, 30 min, 60 min, 120 min, and 24 h (continuous), relative LDH release was 0.017 ± 0.01, 0.62 ± 0.06, 0.57 ± 0.04, 0.65 ± 0.06, and 0.55 ± 0.07 (n = 4 wells each). No statistic significant difference in relative LDH release was detected between the treatment with H2O2 for 10 min, 30 min, 60 min, and 24 h. **p < 0.01 compared with the control group.