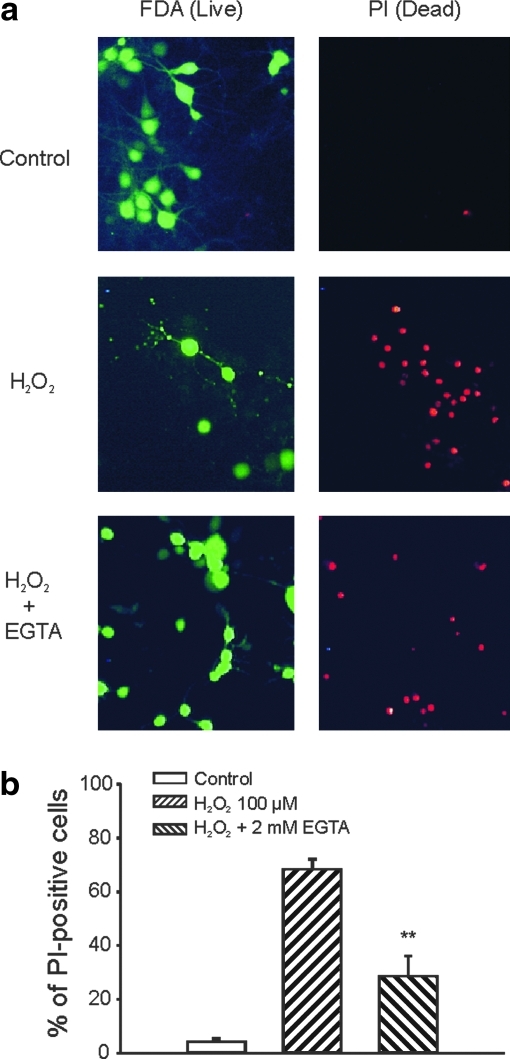
FIG. 3.
Assessment of H2O2-induced injury by fluorescent staining of live and dead neurons. (a) Example images showing fluorescent staining of live (fluorescein-diacetate [FDA]-positive) and dead (propidium iodide [PI]-positive) cells in various treatment groups. Cultured mouse cortical neurons grown on 25 mm glass coverslips were treated with the control medium, the medium containing 100 μM H2O2, or H2O2 plus 2 mM EGTA for 1 h in the presence of MK801, CNQX, and nimodipine. Six hours after the treatment, neurons were incubated in the extracellular solution containing 5 μM FDA and 2 μM PI for 30 min followed by washing with dye-free solution. Live (FDA-positive) and dead (PI-positive) cells were then viewed with fluorescent microscope at excitation/emission wavelength of 500 nm/550 nm for FDA and 580 nm/630 nm for PI staining. (b) Summary data showing the percentage of dead cells in different treatment groups. Images were collected and analyzed using computer software (Bioquant). Two to three fields of at least 50 cells each from individual coverslip were counted for both FDA and PI-positive staining. Six hours after 1 h treatment, percentage of PI-positive cells were 4.3% ± 1.0%, 68.2% ± 3.8%, and 28.5% ± 7.6% for control, H2O2 alone, and H2O2 in the presence of 2 mM EGTA (n = 6–8 fields from two to three coverslips). **p < 0.01 compared with 100 μM H2O2 alone. (To see this illustration in color the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).