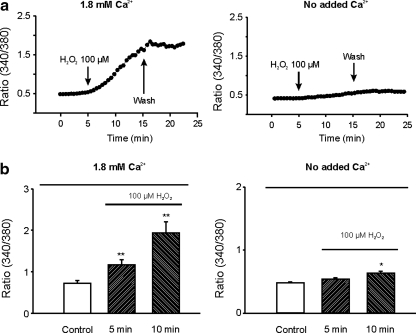
FIG. 5.
Glutamate receptor and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel-independent increase of [Ca2+]i by H2O2. (a) Time-dependent changes of [Ca2+]i in response to bath perfusion of H2O2 in the presence of MK801, CNQX, and nimopidine. Left panel: with bath solution containing 1.8 mM Ca2+, perfusion of 100 μM H2O2 induced a large increase in [Ca2+]i, as demonstrated by an increase in the intensity of 340/380 ratio image. Right panel: with Ca2+ removed from the bath solution, perfusion of 100 μM H2O2 induced only a small increase in the ratio of 340/380 image. (b) Summary data showing the glutamate receptor and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel-independent increase of [Ca2+]i by H2O2. In the presence of 1.8 mM Ca2+ in the bath solution, perfusion of neurons with 100 μM H2O2 for 10 min increased 340/380 ratio from 0.73 ± 0.11 to 1.94 ± 0.26 (166% increase, n = 9, p < 0.01). In the absence of added Ca2+, perfusion of 100 μM H2O2 for 10 min only increased the 340/380 ratio from 0.48 ± 0.02 to 0.63 ± 0.04 (31% increase, n = 12, p < 0.05). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with control.