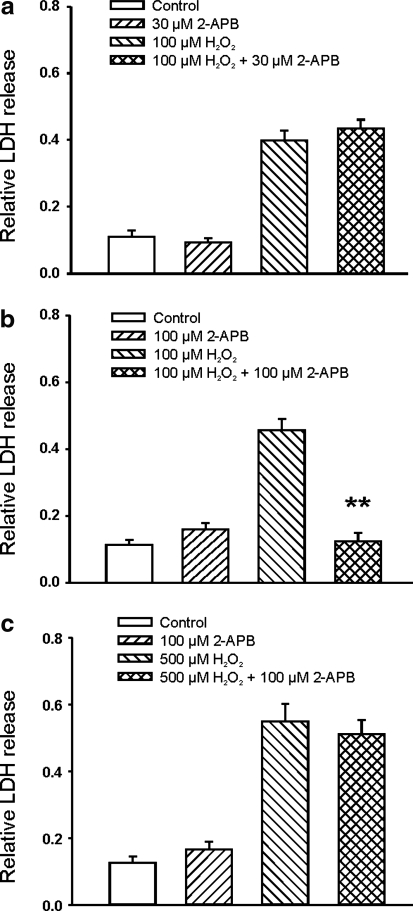
FIG. 7.
Effect of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) on H2O2-induced glutamate-independent injury of mouse cortical neurons. (a) Addition of 30 μM 2-APB, a concentration known to completely inhibit the transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) current but has small effect on the TRPM7 current, did not provide protection against H2O2-induced injury (n = 8 wells each). (b) Addition of 100 μM 2-APB, a concentration known to inhibit the TRPM7 channels, significantly reduced H2O2-induced neuronal injury (n = 15–16, **p < 0.01 compared to 100 μM H2O2 group). (c) Neuronal injury induced by higher concentration of H2O2 (500 μM) was not protected by 100 μM 2-APB (n = 11–12).