Figure 1.
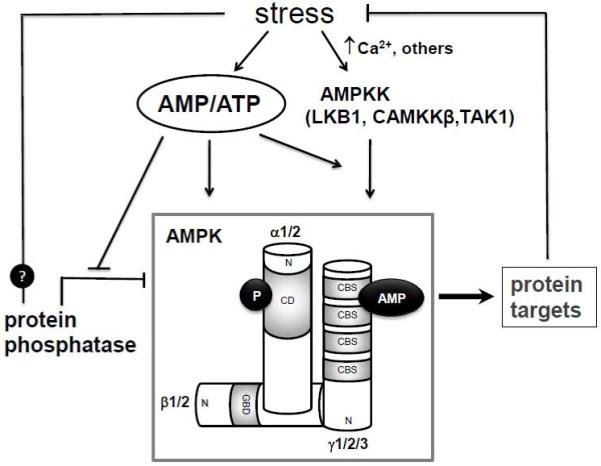
Regulation of the AMPK signaling cascade. The intracellular AMP/ATP ratio is a primary regulator of the system. Increased AMP/ATP activates AMPK via three mechanisms 1) allosteric activation; 2) promotes the Thr 172 phosphorylation of the α- AMPK by its upstream kinase (AMPKK) such as LKB1, and 3) prevents protein phosphatase from dephosphorylating AMPK. Stress can also directly activate the CAMKKβ via increased intracellular calcium levels. It is proposed that certain stresses may directly affect the dephosphorylation process by yet undetermined mechanisms. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; AMPKK, AMPK-kinase; CaMKKβ, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β; TAK1, transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1; CD, catalytic domain; GBD, glycogen binding domain; N, NH2-terminus of subunits; CBS, cystathionine-β-synthase motif.
