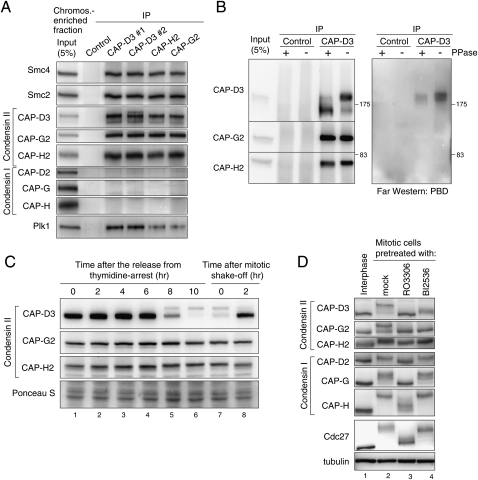
Figure 1.
Regulation of condensin II in mitosis. (A) Immunoprecipitation of Plk1 with condensin II. Condensin II components were immunoprecipitated from a chromosome-enriched fraction prepared from mitotic cell extracts using either of two different antibodies to CAP-D3 (#1 or #2), CAP-G2, CAP-H2, or nonimmune IgG as a control, and resulting precipitates (IP) were analyzed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated. Note that none of the condensin I subunits copurified with the condensin II complex, discounting the possibility that the interaction between condensin II and Plk1 is mediated indirectly by DNA. (B) Plk1 binds directly to CAP-D3 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Immunoprecipitates with either control or CAP-D3 antibodies from mitotic cell extracts were incubated with or without phosphatase (PPase), and were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (left panel) and Far-Western blotting with PBD (right panel). (C) Detection of CAP-D3 phosphorylation in mitotic cell extracts. Synchronized cell populations were analyzed by immunoblotting at the indicated times after the release from thymidine arrest (i.e., early S phase) (lanes 1–6) or nocodazole arrest (i.e., mitosis) (lanes 7,8). As reported previously (Yeong et al. 2003; Lipp et al. 2007), slowly migrating bands of CAP-D3 were detected specifically during mitosis, but little retardation was detectable for CAP-G2 and CAP-H2. (D) Mitotic phosphorylation of condensin II depends on Cdk1 and Plk1. Thymidine-arrested interphase cells (lane 1), nocodazole-arrested mitotic cells (lane 2), a Cdk1 inhibitor RO3306-treated nocodazole-arrested mitotic cell (lane 3), or a Plk1 inhibitor BI2536-treated nocodazole-arrested mitotic cell (lane 4) were analyzed by immunoblotting for condensin subunits. The mobility shifts for Cdc27 verify that these pretreatments efficiently abolished the activities of the targeted kinases in mitotic cells (Kraft et al. 2003).