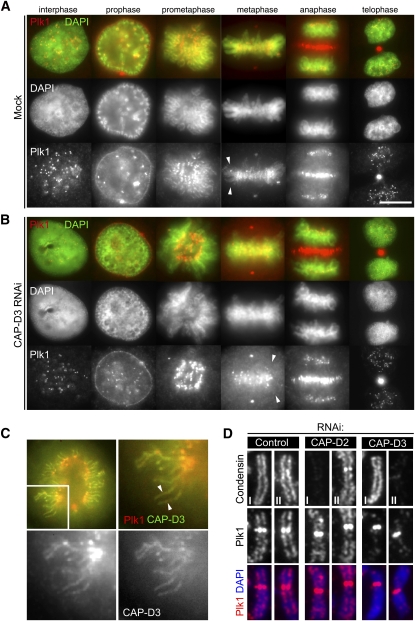
Figure 3.
Enrichment of Plk1 on chromosomal axes. (A) Localization of Plk1 by immunofluorescence microscopy. Exponentially growing HeLa cells were fixed with methanol, incubated with antibodies to Plk1, and labeled with an Alexa fluorescent dye (red). DNA was stained with DAPI (green). Representative cells in interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase are shown. Note the chromosome axial staining with Plk1 antibodies in prometaphase and metaphase (arrowheads). Bar, 10 μm. (B) Enrichment of Plk1 on chromosome axes is lost in the absence of CAP-D3. Cells depleted of CAP-D3 were processed for immunofluorescence microscopy as in A. Note that Plk1 signals on chromosome axes are displaced (arrowheads), while the other localizations are preserved. (C) Colocalization of Plk1 with CAP-D3. Wild-type GFP-CAP-D3-expressing cells were fixed and stained with Plk1 antibodies. Both CAP-D3 (right bottom panel; green in top merged panels) and Plk1 (left bottom panel; red in top merged panels) signals are visible on chromosome axes. (D) Enrichment of Plk1 at chromosome axes depends on condensin II but not condensin I. Chromosome spread samples prepared from mitotic cells that had been depleted of CAP-D2, CAP-D3, or mock (control) were fixed and stained for Plk1 with either condensin I (CAP-H) or condensin II (CAP-D3), as indicated. Quantification of fluorescence intensities for Plk1 signals is shown in Supplemental Figure 5A.