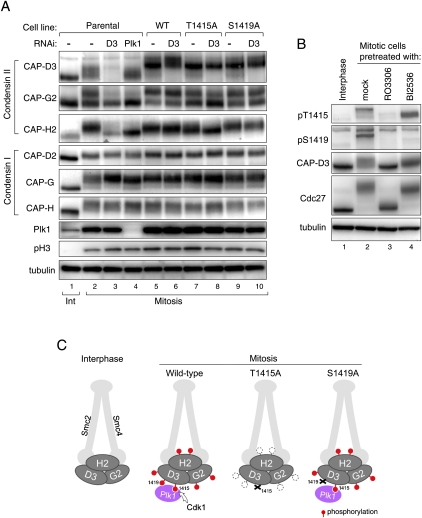
Figure 6.
Cdk1-mediated phosphorylation of Thr 1415 is required for the full phosphorylation of condensin II. (A) Mitotic phosphorylation of non-Smc subunits of condensin II is perturbed in the T1415A mutant. Mitotic cell extracts prepared from indicated cell lines, with or without RNAi to Plk1 or to CAP-D3, were analyzed with the antibodies to condensin subunits. Parental cell line indicates the cell population that does not express any tagged protein. Note that changes in phosphorylation levels, as seen for condensin II subunits, are not readily detectable for condensin I subunits. (B) Phosphorylation of Thr 1415 and Ser 1419 depends primarily on Cdk1 and Plk1, respectively. Total cell extracts were prepared from thymidine-arrested interphase cells (lane 1) or nocodazole-arrested mitotic cells (lanes 2–4) in which the activity of Cdk1 or Plk1 is inhibited by RO3306 or BI2536 treatment, respectively (lanes 3,4), and were analyzed by immunoblotting using the antibodies indicated. Note that pT1415 and pS1419 antibodies can hardly detect CAP-D3 protein in interphase cells (cf. lanes 1 and 2), indicating the specific reactivity of these antibodies to mitotic phosphorylated forms. (C) Illustrations depicting how condensin II complex is phosphorylated in mitosis, and how phosphorylations are affected in the T1415A and S1419A mutants. The model predicts the crucial role of Cdk1 in phosphorylating CAP-D3 at Thr 1415, which triggers the full phosphorylation of the condensin II complex, and explains why the phosphorylation levels are markedly decreased in T1415A-replaced but not S1419A-replaced cells.