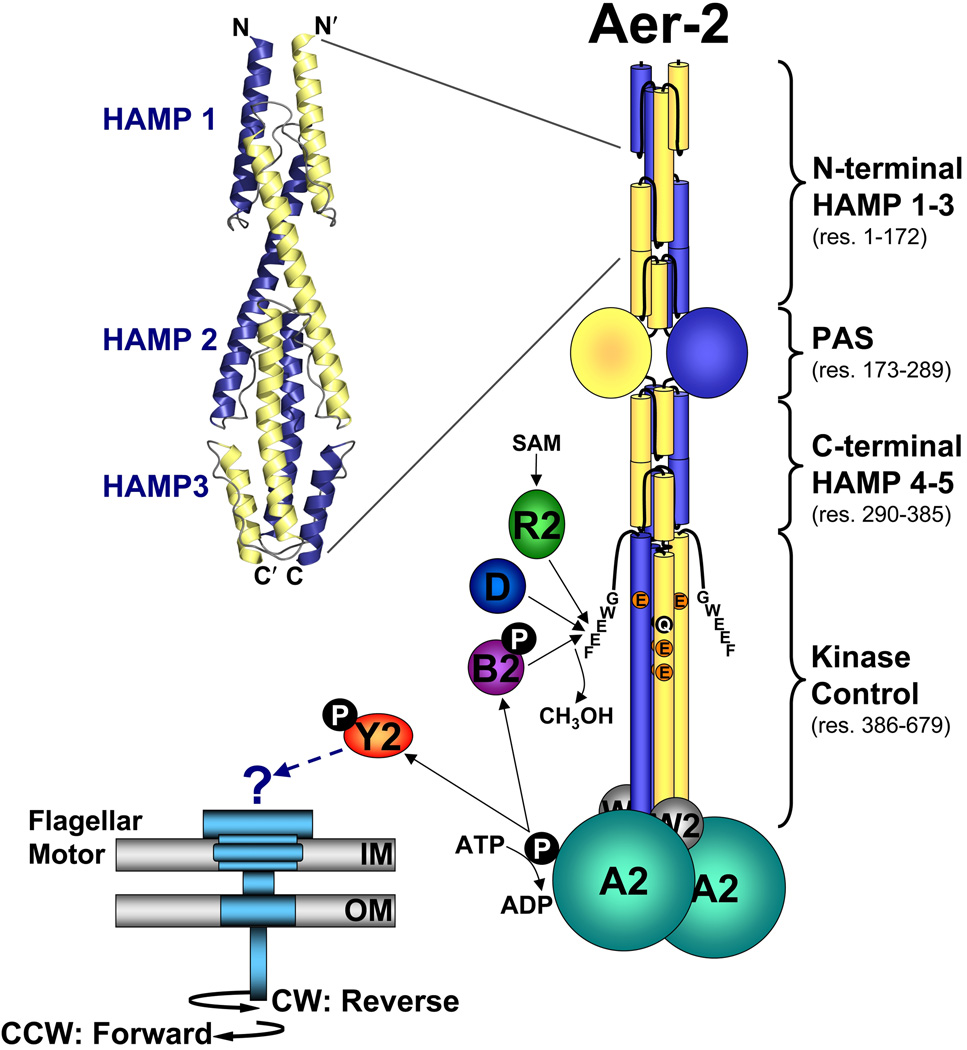
FIG. 1.
Cartoon showing the proposed domain organization of an Aer-2 dimer and the proteins associated with the Cluster II chemotaxis-like system. Each Aer-2 monomer contains three N-terminal HAMP domains, followed by a PAS sensing domain, two C-terminal HAMP domains, and a C-terminal kinase control domain. The structure of the three N-terminal HAMP domains was recently solved by x-ray crystallography [3LNR (Airola et al., 2010)]. By analogy to other methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins, the kinase control domain is predicted to contain four methylation sites (QEEE, res. 414, 421, 428 and 610) and a C-terminal pentapeptide (GWEEF, res. 675–679) for binding the adaptation enzymes CheR2, CheB2 and CheD. Aer-2 is also predicted to form a ternary complex with the CheA2 and CheW2 proteins. The binding of an oxy-gas ligand to the Aer-2 PAS-heme domain is expected to alter the autophosphorylation rate of CheA2 and the subsequent transfer of phosphate to CheY2. It is currently unclear whether phospho-CheY2 binds to the flagellar motor or whether it interacts with a different response system. Abbreviations: A, W, Y, R, B, and D, Che proteins; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane; CW, clockwise; CCW, counterclockwise.