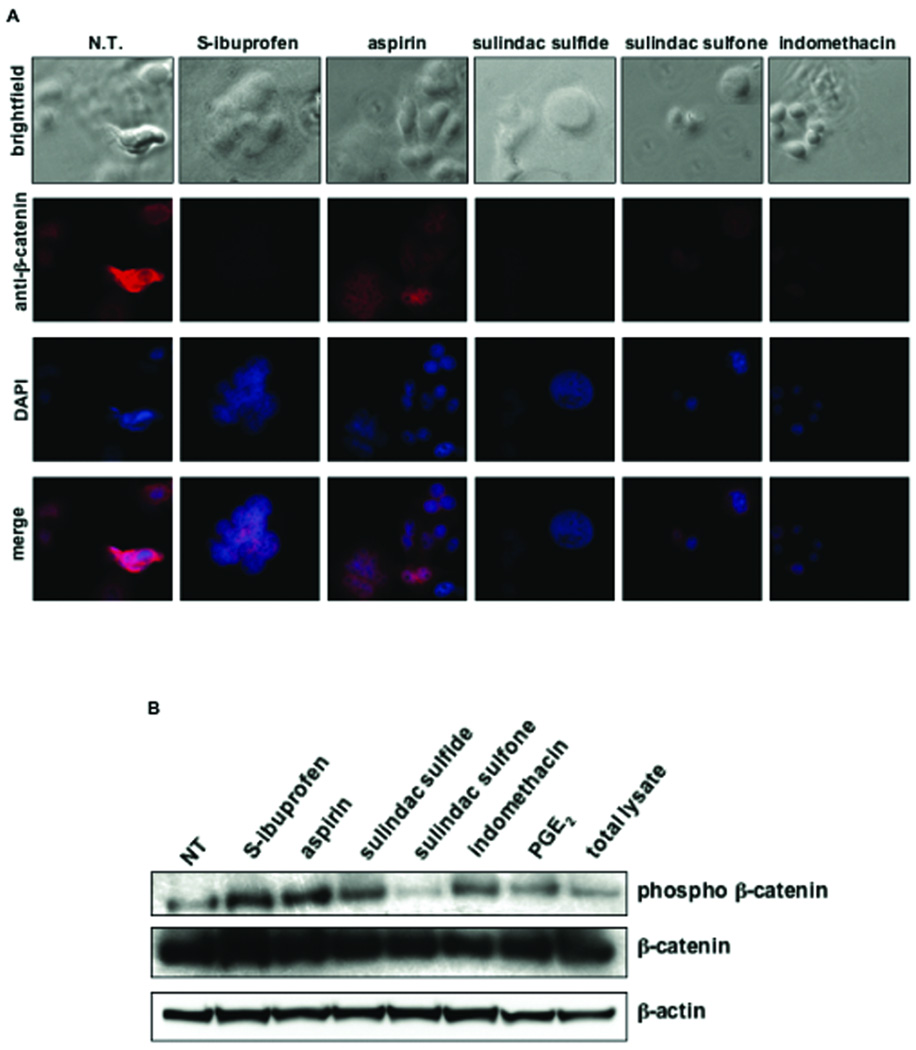
Figure 3. S-ibuprofen inhibits β-catenin expression and nuclear localization in SW480 colon cancer cells.
A, Immunofluorescence microscopy of β-catenin (Alexa Fluor 568, red) in SW480 cells following treatment with a panel of NSAIDs (1 mM S-ibuprofen, 5 mM aspirin, 100 µM sulindac sulfide, 600 µM sulindac sulfone and 600 µM indomethacin) for 24 hours as described in Materials & Methods. Nuclei were counter-stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). Merged images represent the overlay of the image at 603 nm (β-catenin, Alexa Fluor 568) with the image at 488 nm (DAPI). B, Western blot analysis of phospho-β-catenin and total β-catenin in the cytoplasmic fraction of SW480 cells following 24-hour treatment with a panel of NSAIDs (S-ibuprofen, aspirin, sulindac sulfide, sulindac sulfone and indomethacin). PGE2 was added as a negative control. Total cell lysates from SW480 cells containing both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions is also included as a negative control. Blots were re-probed with anti-β-actin as a loading control.