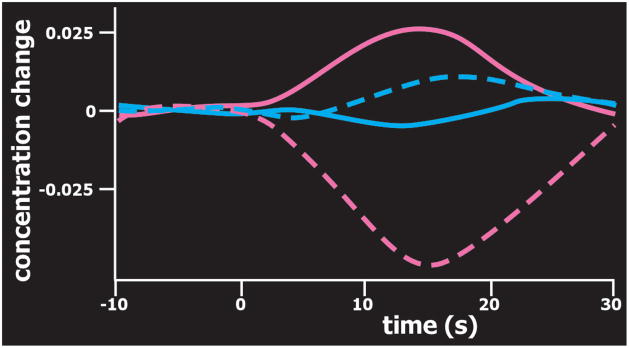
Figure 3.
Optical imaging is based on task-related brain activation-induced focal changes in the concentration of oxyhemoglobin (pink) and deoxyhemoglobin (blue). Illustrated here are data from two regions of interest (three detectors each, approximate areas sampled indicated by yellow circles on cover) averaged across eight subjects performing simple mental arithmetic (adapted from Pfurtscheller et al.1). Oxyhemoglobin was focally increased in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (pink, solid line) and decreased in the anterior prefrontal cortex (pink, dashed line). As noted by the authors, these results are consistent with findings from EEG and fMRI studies, and may be indicative of focal activation with surround deactivation.