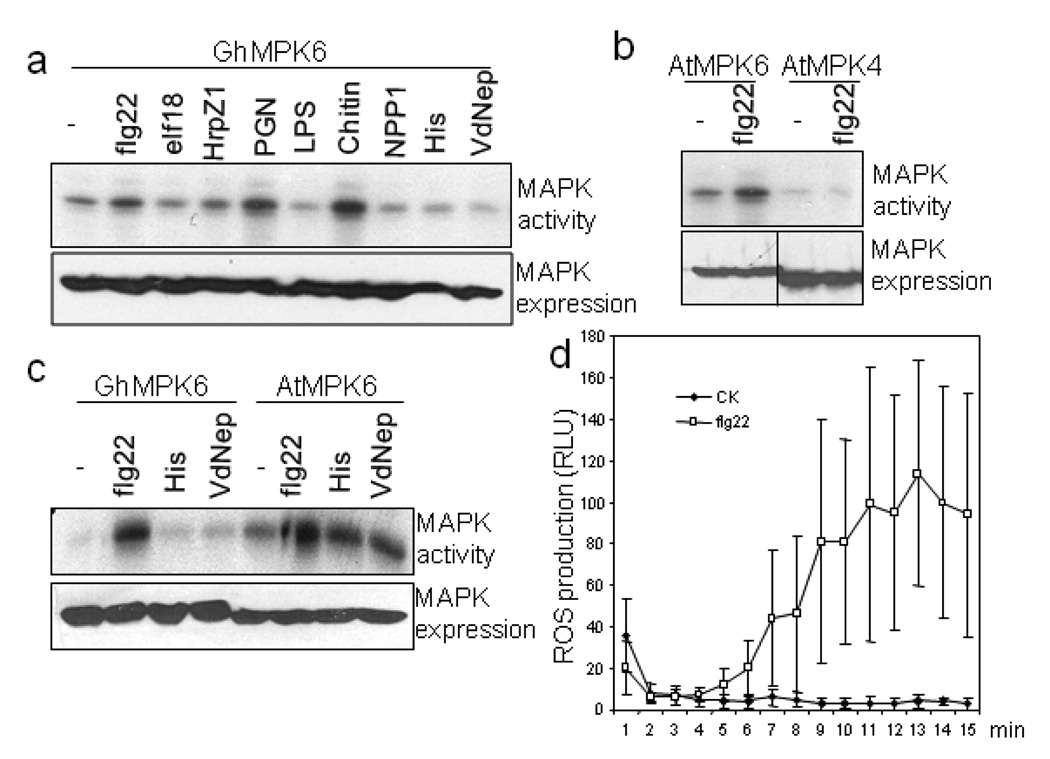
Figure 6. Cotton protoplasts respond to multiple PAMPs and elicit convergent defense signaling.
a. flg22, PGN and Chitin activate GhMPK6 in cotton protoplasts. The protoplasts were transfected with GhMPK6, and incubated for 6 hr before treatment with different PAMPs for another 10 min. The concentrations of individual PAMPs are flg22, 1 uM; elf18, 1 uM; HrpZ1 harpin, 100 nM; PGN, 50 µg/ml; chitin, 50 µg/ml; LPS, 50 µg/ml; NPP1, 20 nM; VdNEP, 20 nM. His is the control of His-VdNEP. The top panel shows the MAPK activity detected by phosphorylation of MBP substrate, and the bottom panel is GhMPK6 expression detected by Western blot with an anti-HA antibody. b. flg22 activated AtMPK6, but not AtMPK4, in cotton protoplasts. c. flg22 activated GhMPK6 in Arabidopsis protoplasts. “-“ is the H2O control for flg22 and His is the control of His-VdNEP. d. ROS burst in cotton leaves triggered by flg22 treatment. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. The data in (d) are shown as means ± standard errors from ten independent biological replicates.