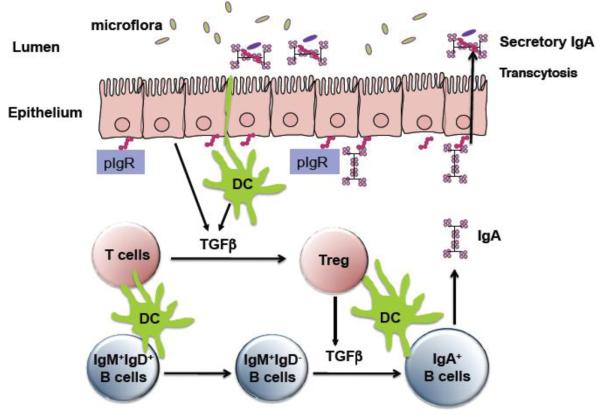
Figure 1. Treg cell-IgA axis maintains intestinal homeostasis to microbiota and protect the mice from intestinal inflammation.
Upon activation, Treg cells produce TGF-β which promotes B cell IgA class switching and IgA production in mucosa. IgA then binds polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on epithelial cells to be transported into intestinal lumen. The major role of IgA is to maintain a balance between the host and its microbiota.