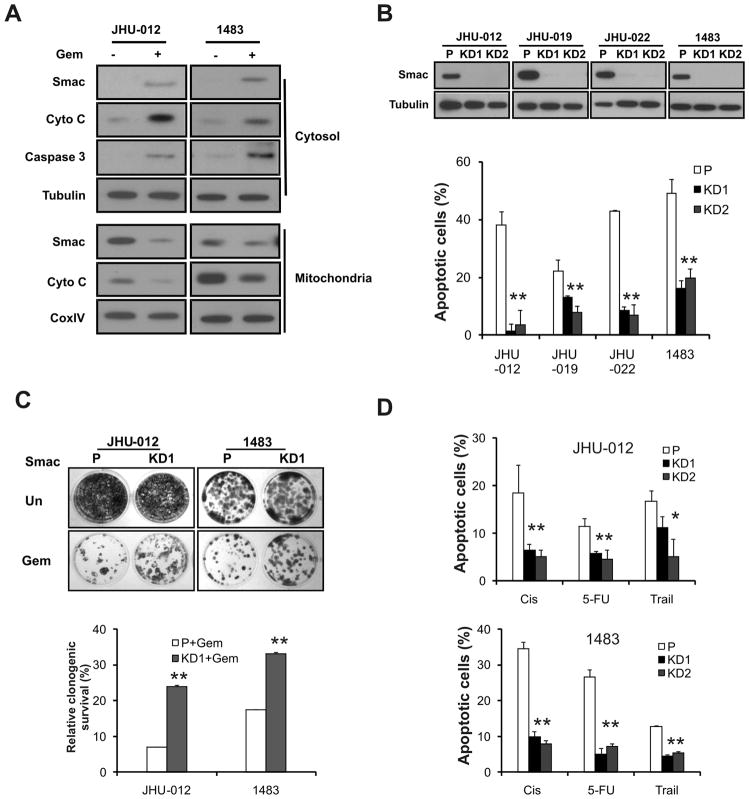
Figure 1. Smac mediates apoptosis induced by therapeutic agents in HNSCC cells.
(A) Gemcitabine induced release of Smac and cytochrome c, and activation of caspase 3. JHU-012 and 1483 cells were treated with 50 μM gemcitabine for 48 h. Smac and cytochrome c in the cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were analyzed by Western blotting. Tubulin and CoxIV were used as controls for fraction and loading. (B) SMAC knockdown blocked gemcitabine-induced apoptosis. Upper, examples of stable knockdown of SMAC clones in indicated HNSCC lines were identified by Western blotting. Lower, apoptosis was analyzed by nuclear fragmentation assay. P-parental cells; KD1, KD2- two independent knockdown clones. (C) SMAC knockdown enhanced clonogenic survival of HNSCC cells following gemcitabine treatment. JHU-012 and 1483 cells were treated by 10 μM gemcitabine or left untreated for 6 h, then plated at 1:500 dilution (~400 cells per well) in 12-well plates and allowed to form colonies for 14 days. Upper panel, representative pictures of the colonies. Lower panel, the colonies containing >50 cells were enumerated and relative survival calculated with untreated cells set at 100%. (D) SMAC knockdown blocked apoptosis induced by multiple therapeutic agents. JHU-012 and 1483 cells were treated with indicated agents for 48 h. Apoptosis was measured by nuclear fragmentation assay. Cis, cisplatin (50 μM), 5-FU, 5-Fluorouracil (50 μg/mL) and Trail (100 ng/mL). **, P < 0.01, *, P < 0.05, KD vs. P.