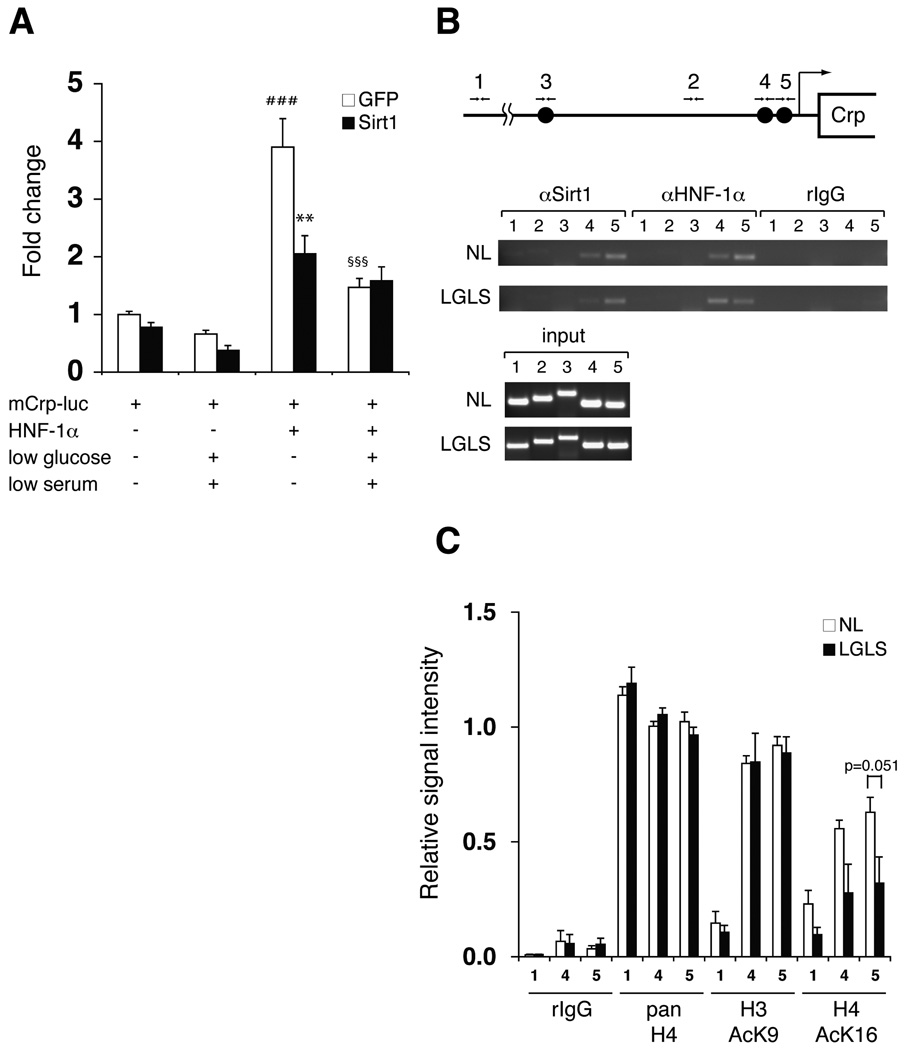
Figure 4. Suppression of HNF-1α-mediated transcriptional activation of the Crp promoter by Sirt1.
(A) Nutrient restriction and Sirt1 suppress HNF-1α-mediated activation of the Crp promoter. Primary hepatocytes were infected with GFP- or Sirt1-expressing adenoviruses, transfected with pGL3-mCrp-1777 (mCrp-luc) and HNF-1α expression or control vectors, and cultured in normal or LGLS media as indicated for 48 hours prior to extract collection. Luciferase activity was normalized to protein concentration. Results are shown as mean values ± SEM (n=3, ###p<0.001, compared to GFP-expressing cells transfected with mCrp-luc under normal and LGLS media; **p<0.01 (p=0.001), §§§p<0.001, compared to GFP-expressing cells transfected with mCrp-luc and HNF-1α under normal media, by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer post hoc test). (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) for the Sirt1-HNF-1α complex on HNF-1α binding sites in the mouse Crp promoter. Chromatin-DNA adducts were extracted from mouse primary hepatoctyes cultured in normal media (NL) or media with low glucose and serum (LGLS). After immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies, DNA was purified and amplified by PCR with the following primer sets: primer sets 1 and 2 for control regions located ~5 kb and 965bp upstream of the transcription start site, respectively; primer set 3 for a region containing a distal HNF-1α binding site located 1.8-kb upstream; primer sets 4 and 5 for regions containing proximal HNF-1α binding sites locate 273 bp and 113 bp upstream, respectively. (C) Quantitation of ChIP for acetylated histones H3 and H4 under normal and nutrient-restricting conditions. Chromatin-DNA adducts were extracted from mouse primary hepatoctyes cultured in normal media (NL) or media with low glucose and low serum (LGLS) and immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies. After PCR amplification, band intensities were quantitated and normalized to the signal intensity of each input. Relative signal intensity is shown for primer sets 1, 4, and 5 as mean values ± SEM. The results were assessed by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer post hoc test (n=4).