Figure 4.
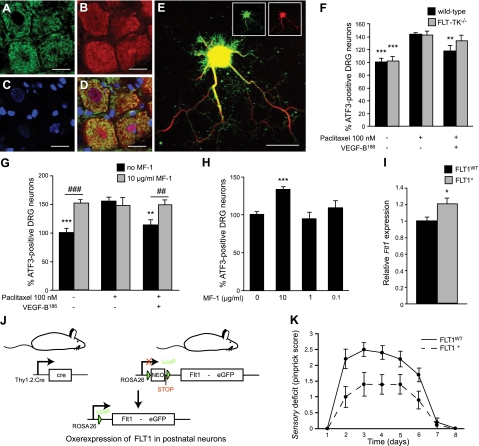
FLT1 is a functional VEGF-B receptor in the nervous system. A–D) FLT1 expression is detected on DRG neurons, as revealed by double immunostaining (D) on cryounfixed sections for endogenous Flt1 (sc-9029 antibody; A) and the neuronal marker NEUN (B). Nuclear dye DAPI (C) colocalizes with NEUN and FLT1 staining. E) FLT1 expression on DRG neurites was confirmed in vitro using double immunostaining for FLT1 (sc-316, green) and the neurofilament antibody 2H3 (red). F) Neuroprotective effects of VEGF-B186 on DRG neurons depend on FLT1 tyrosine-kinase activity: recombinant VEGF-B186 (50 ng/ml) is capable of reducing ATF3 immunoreactivity in primary DRG neurons from WT mice (P<0.01), but not in primary DRG cultures isolated from FLT-TK−/− mice (n=12 wells from 3 mice/genotype; P=NS). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. 100 nM paclitaxel. G) MF1, a neutralizing FLT1 antibody, inhibits the neuroprotective activity of VEGF-B186 on primary DRG neurons: VEGF-B186 reduces 100 nM paclitaxel-induced ATF3 immunoreactivity from 154.9 ± 7.7 to 113.3 ± 9.5%, whereas the addition of MF1 blocks this effect by increasing ATF3 immunoreactivity again to 148.7 ± 9.0% even in the presence of 50 ng/ml VEGF-B186 (n=6 wells from 3 rats). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. 100 nM paclitaxel; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 as indicated. H) Addition of 10 μg/ml FLT1-neutralizing antibody MF1 increases neuronal stress in primary DRG cultures. ATF3 immunoreactivity: 133.1 ± 4.4 vs. 100.0 ± 4.0% in untreated cultures. Lower doses of MF1 did not exhibit an effect. ***P < 0.001 vs. control. I) Strategy for the generation of a transgenic mouse line, in which FLT1 is selectively overexpressed in postnatal neurons. The Flt1 cDNA is cloned downstream of a floxed STOP sequence and upstream of an IRES sequence followed by an enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) marker. Transgenic mice expressing this construct under control of the endogenous ROSA promoter are subsequently generated (stoplox/loxFLT1 mice). In the absence of Cre, ROSA promoter activity is blocked by an in-frame STOP sequence resulting in no overexpression of Flt1 (FLT1WT mice). In the presence of the Cre protein, which is expressed in postnatal neurons under control of the Thy1.2 promoter, the STOP sequence is excised, resulting in increased expression of Flt1 (FLT1+ mice). *P < 0.05. J) Flt1 expression levels are 20% higher in whole DRGs from FLT1+ mice compared to FLT1WT mice (n=8–10/group; P<0.05). K) Neuronal overexpression of FLT1 protects mice from developing a severe sensory deficit (n=10/group; P<0.01). Mean ± se pinprick scores are shown to visualize the sensory deficit in time. Scale bars = 20 μm.