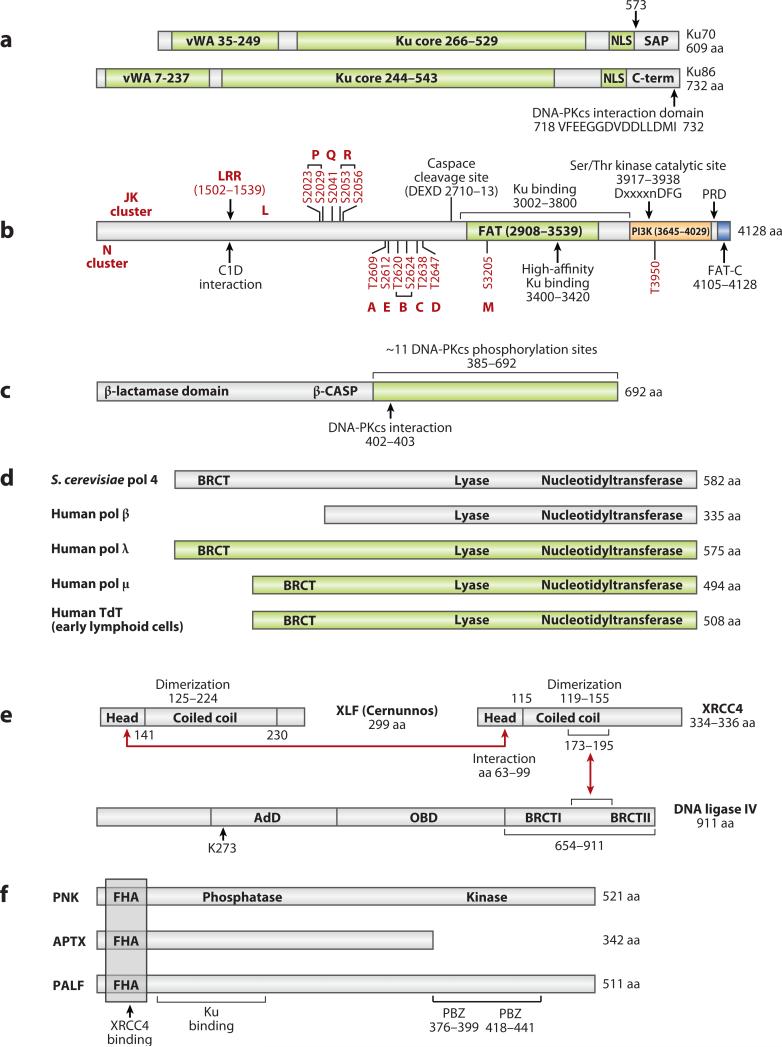
Figure 4. Diagrams of Domains within NHEJ Proteins.
a. Ku is a heterodimer of Ku70 and 86. vWA designates von Willebrand domains. SAP designates a SAF-A/B, Acinus, and PIAS domain and may be involved in DNA binding.
b. DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation sites are shown in red (90, 95, 96). The function of each phosphorylation site (A-E, L, M, P-R) and cluster (N and JK) are still under study. Adjacent phosphorylation sites that are linked by a bracket have not been functionally dissected from one another. LRR designates the leucine-rich region. The FAT-C domain is a FAT domain at the C-terminus. PI3K designates the PI3 kinase domain. PRD designates the PI3K regulatory domain.
c. Artemis is phosphorylated by DNA-PKcs at 11 sites within the C-terminal portion (green) (162, 163). Amino acids 156 to 385 share conserved sequence with those metallo-β-lactamases that act on nucleic acids (164). This region has been called the β-CASP domain (metallo-β-lactamase-associated CPSF Artemis SNM1 PSO2) (165).
d. POL × polymerase family. Pol mu and pol lambda are involved in NHEJ in mammalian somatic cells generally. TdT is only expressed in early lymphoid cells where it participates in NHEJ primarily in the context of V(D)J recombination.
e. The NHEJ ligase complex consists of XLF (Cernunnos), XRCC4, DNA ligase IV. The red arrows indicate the regions of physical interaction (118, 119). OBD in ligase IV is the oligo-binding domain, and AdB is the adenylation domain.
f. Polynucleotide kinase (PNK), Aprataxin (APTX), and PALF (APLF) are ancillary components that bind to XRCC4 of the ligase complex. The PBZ domain appears to be important for PARP-1 binding, for poly-ADPribose binding, and for nuclease activity. FHA designates the forkhead-associated domain.