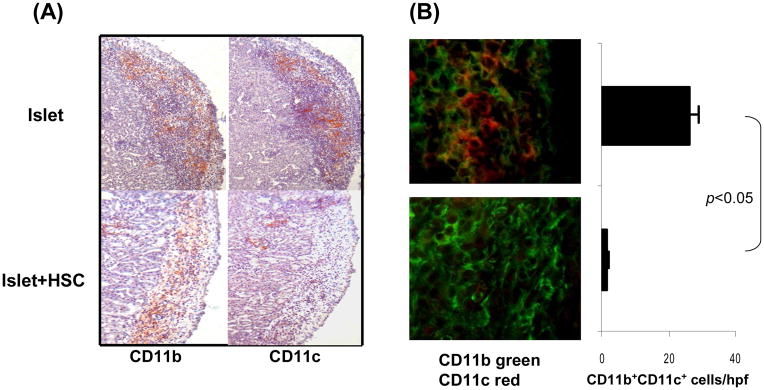
Figure 1. Impact of cotransplantation HSC on development of myeloid cells.
300 BALB/c (H-2d) islets were mixed with 5 × 105 HSC from B6 (H-2b) mice, and transplanted under renal capsule of STZ-induced diabetic B6 recipients (islet allografts alone served as control). The animals were sacrificed on post operative day (POD) 7 (n=3 in each group). (A) Islet graft cryostat sections were stained with anti-CD11b or -CD11c mAbs. The color was developed by an enzyme reaction using avidin-biotin-alkaline phosphatase complex as the substrate (red). (B) Islet graft cryostat sections were double stained with anti-CD11b (green) and -CD11c (red) mAbs, and evaluated under a fluorescent microscope. The double positive cells were counted in total 10 high power fields (hpf) that were randomly selected in each graft. The data are expressed as mean CD11b+CD11c+ cells/graft ± 1SD. (C) Cells isolated from the islet/HSC and islet alone grafts were multiple color stained with specific mAbs against CD45, CD11b and CD11c or the indicated key cell surface molecules for flow analyses. Expression of CD11b and CD11c was analyzed in CD45+ and CD45− populations. Expression of cell surface molecules were analyzed gated on CD11b+ cells in both groups, and demonstrated as histograms (filled area is isotype control). The number is percentage of the positive cells. The data are representative of three separated experiments.