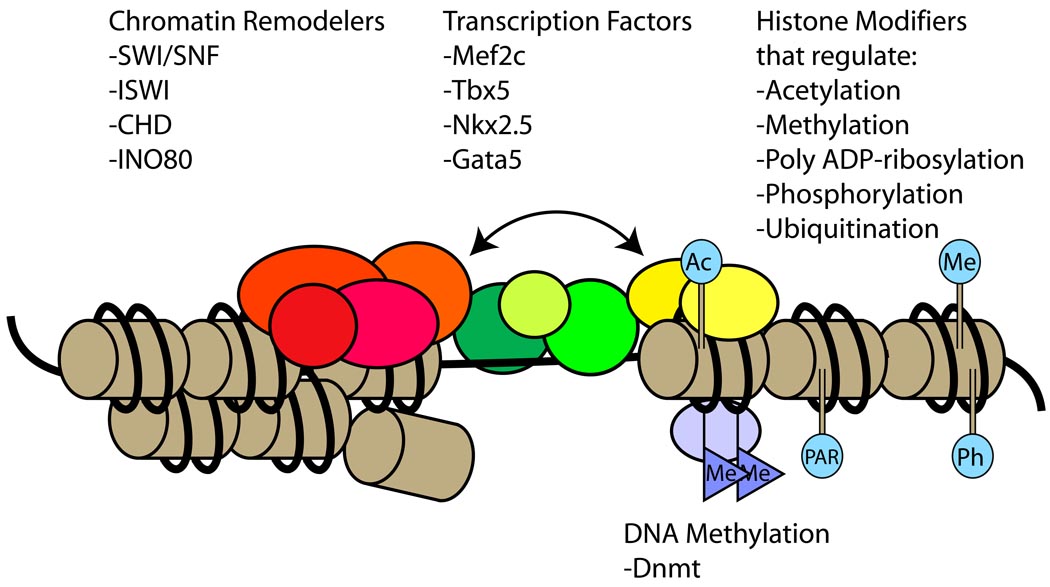
Figure 2. Interactions among chromatin regulators and transcription factors to control gene expression.
Chromatin regulation is an epigenetic mechanism that controls gene expression and function without changes in the DNA sequence. Chromatin remodelers use energy derived from ATP hydrolysis to change chromatin architecture. Histones are covalently modified to modulate access of transcription factors to genomic loci. DNA can be methylated to control transcription. These different forms of chromatin modification often act in concert and are co-regulated to control expression of cardiac genes. Ac: acetylation. Me: methylation. Ph: phosphorylation. PAR: poly ADP-ribosylation. Red/Orange: chromatin remodellers. Yellow: histone modifiers. Purple: DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt). Green/Olive: transcription factors.