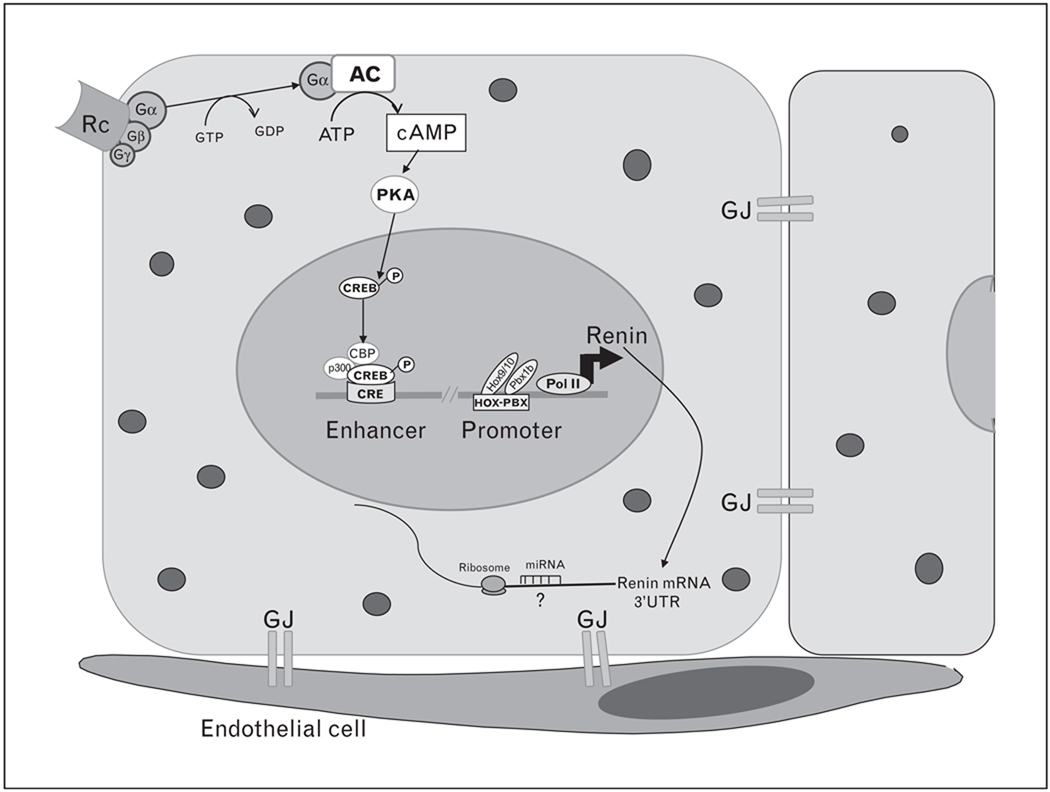
Figure 1. Major events in renin expression.
Activation of a G protein-coupled Rc by its ligand leads to conformational change transmitted to a G protein complex. The Gsα subunit is released from the complex after conversion of GTP to GDP and activates the AC, which in turn converts ATP in the second messenger cAMP. cAMP activates PKA that phosphorylates the CREB in the nucleus. Phosphorylated CREB recruits CBP and p300 and binds to the CRE in the enhancer region of the renin promoter, switching on renin mRNA transcription. At the proximal promoter, Hox and Pbx 1b paralogs bind to the HOX–PBX site and also initiate renin transcription. Posttranscriptional regulation at the 3’UTR occurs by binding proteins that increase renin mRNA stability (not depicted) and by miRNA, which repress renin translation, degrade renin mRNA or both. cAMP also stimulates renin release (not depicted). For ease of reading most of the binding sites and their interactions along the promoter are not depicted. AC, adenylyl cyclase; cAMP, cyclic AMP; CRE, cAMP responsive element; CREB, cAMP responsive element binding protein; GJ, gap junction; miRNA, microRNA; PKA, protein kinase A; Pol II, polymerase II; Rc, receptor; UTR, untranslated region.