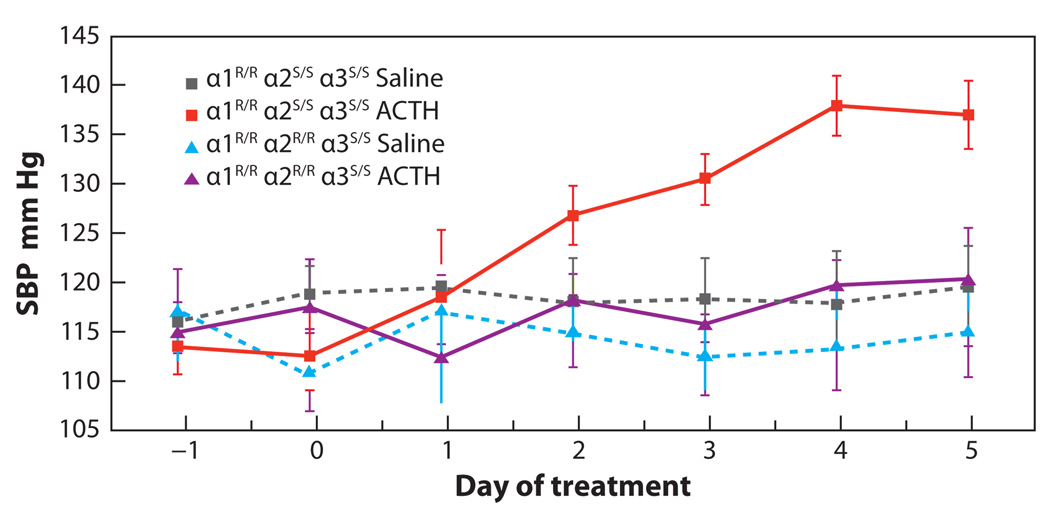
Figure 2.
ACTH-induced hypertension is dependent on the ouabain-binding site of α2 isoform of the Na,K-ATPase. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was measured in wild-type mice α1R/Rα2S/S and genetically engineered mice with an ouabain-resistant α2 isoform, α1R/Rα2R/R, before and during treatment with ACTH. Mice with either of these two genotypes were also injected with saline to serve as controls. Although animals with an α1R/Rα2S/S genotype exhibited an increase in blood pressure following administration of ACTH, those with the α1R/Rα2R/R genotype failed to increase blood pressure following ACTH administration. The blood pressure of mice with either of the two genotypes did not increase with saline administration. These studies clearly demonstrate that the ouabain-binding site of the α2 isoform of the Na,K-ATPase is required for ACTH-induced hypertension in mice. This figure is modified from figure 1a of Reference 126.