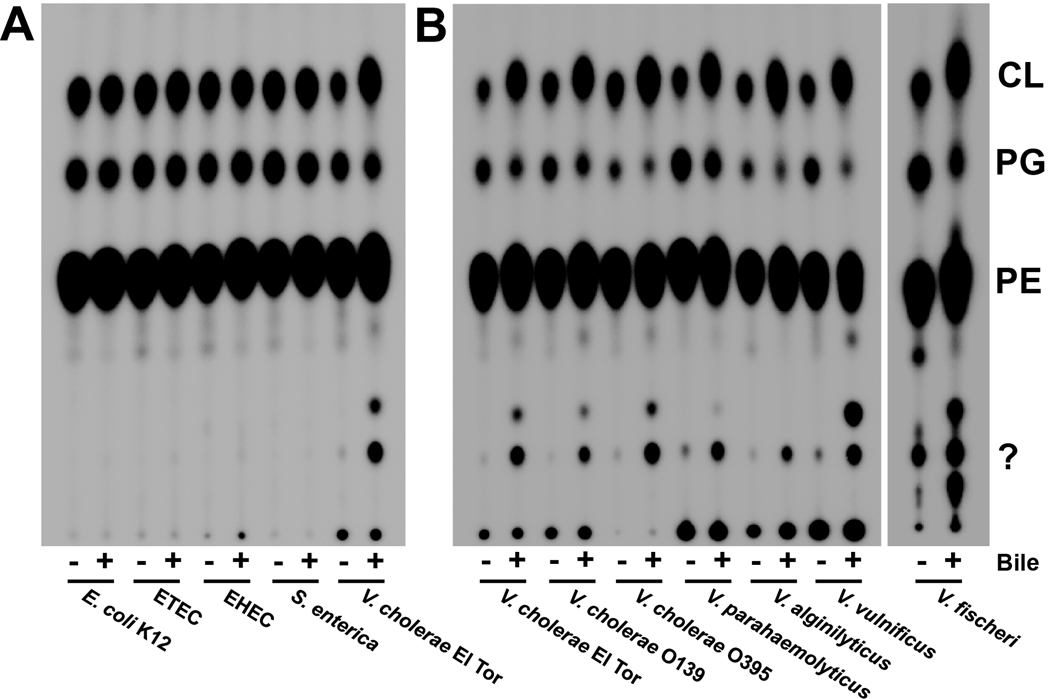
Fig. 2. Comparison of the phospholipid profiles of E. coli, S. enterica and Vibrio species grown in the presence and absence of bile.
A. V. cholerae exhibits a different phospholipid profile than three E. coli strains and S. enterica serovar Typhimurium when grown in the presence of bile. ETEC, enterotoxigenic E. coli; EHEC, enterohaemorrhagic E. coli. Density analysis (Quantity One) indicated no significant quantitative change between the levels of the three major PLs in E. coli and Salmonella, whereas the same analysis for V. cholerae El Tor revealed significant increases (two-fold) in CL, decreases in PG and increases in two minor PLs. Densitometry data can be found in Table S2.
B. The altered phospholipid profile following bile exposure is observed in several Vibrio species.