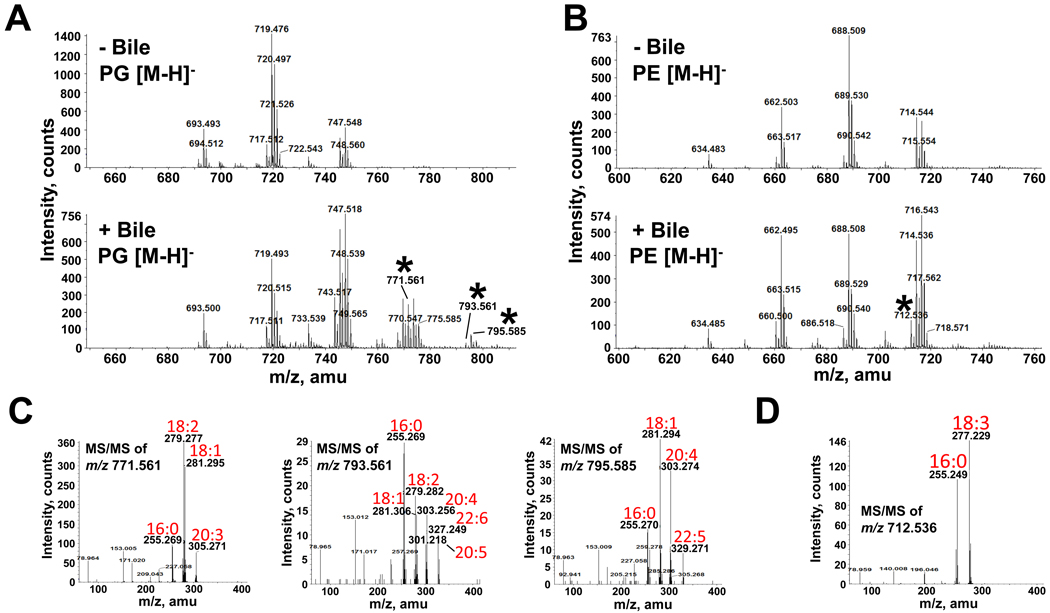
Fig. 7. Mass spectrometric analysis of PG and PE extracted from V. cholerae grown in the presence and absence of bile.
A and B. Negative-ion ESI-MS of [M-H]− ions of V. cholerae PG (A) and PE (B) isolated from cultures grown in the presence and absence of bile. Selected peaks (*) found only in the presence of bile were subsequently analyzed by MS/MS.
C. Negative-ion MS/MS of the PG [M-H]− ions at m/z 771.561, 793.561 and 795.585 detected only in the presence of bile. These product-ion spectra revealed the presence of numerous long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (18:2, 20:3, 20:4, 22:5 and 22:6) as constituent of PG.
D. Negative-ion MS/MS of the PE [M-H]− ion at m/z 712.536 detected only in the presence of bile. This product-ion spectrum revealed the presence of a fatty acid (18:3) unique to bile.