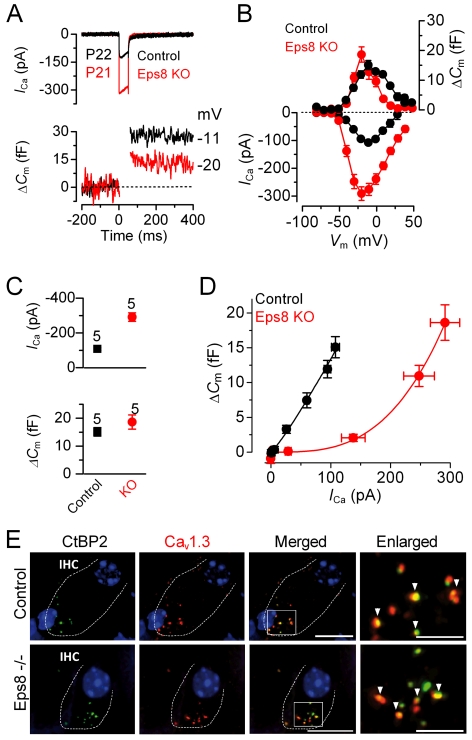
Figure 8. Exocytotic Ca2+ dependence and synaptic organization in Eps8 IHCs.
(A and B) I Ca and ΔCm responses from adult control and Eps8 knockout IHCs. Recordings were obtained in response to 50 ms voltage steps, in 10 mV increments, from −81 mV. For clarity, only maximal responses are shown in (A). (C) Maximal peak I Ca (top panel) and ΔC m (bottom panel) values, from P22 control and P21 knockout IHCs. (D) Synaptic transfer relations obtained by plotting ΔC m against the corresponding I Ca between −71 mV and the peak I Ca from panel B, showing that knockout IHCs exhibited a steeper intrinsic Ca2+ dependence of exocytosis than control cells [42]–[45]. Fits are according to eqn. 1 (see Methods). (E) Immunolabeling of synaptic ribbons (green: CtBP2/RIBEYE) and CaV1.3 Ca2+ channels (red) at the presynaptic site of control (top panels) and knockout (bottom panels) adult IHCs (enlarged images magnified in the right panels). A comparable degree of colocalization was present in IHCs from both genotypes (indicated by the yellow overlapping staining and arrowheads in the right panels). Scale bars: 10 µm, apart from the two enlarged panels, where they are 5 µm.