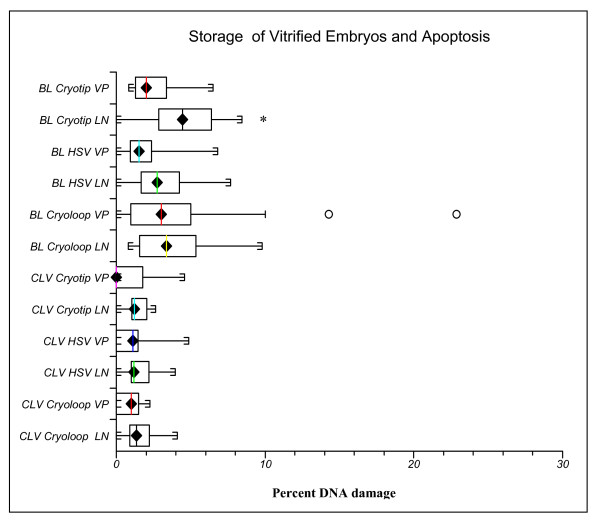
Figure 3.
Cleavage and blastocyst stage embryos were vitrified in different carriers and stored in liquid nitrogen (LN) or held in the vapor phase (VP) of a liquid nitrogen dry shipper for 96 hours to simulate transport conditions. Upon warming, DNA damage was assessed by quantification of the percentage of blastomeres per embryo exhibiting DNA fragmentation. The only carrier to exhibit a difference was the Cryotip, with a significantly higher percentage of DNA damage with blastocyst storage in the liquid phase. *P = 0.004. The percentage of DNA damage was significantly higher with vitrification of blastocysts versus cleavage stage embryos (P < 0.001).